
Eavesdroppers can hack 6G frequency with DIY metasurface
Rice engineers discovered 6G wireless “pencil beams” are vulnerable to eavesdroppers armed with DIY metasurfaces.

Eavesdroppers can hack 6G frequency with DIY metasurface
Rice engineers discovered 6G wireless “pencil beams” are vulnerable to eavesdroppers armed with DIY metasurfaces.

Sophisticated fluid mechanics model is on a roll
Engineers at Rice and Waseda universities produce a video simulation to illustrate the complex aerodynamics around a moving car and its tires.

Computational sleuthing confirms first 3D quantum spin liquid
Physicists have confirmed the first 3D quantum spin liquid, a solid material with a liquidlike magnetic state.
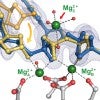
Crystal study may resolve DNA mystery
Rice University bioscientists have uncovered a tiny detail that could help understand how DNA replicates with such astounding accuracy.

Daniel Preston wins NSF CAREER Award
Daniel Preston wins a National Science Foundation CAREER Award to develop textile-based wearable robots.

Rice ‘metalens’ could disrupt vacuum UV market
Rice photonics researchers have created a potentially disruptive technology for the ultraviolet optics market.

Subtle racial slights at work cause job dissatisfaction, burnout for Black employees
Black employees face a host of subtle verbal, behavioral and environmental slights related to their physical appearance, work ethic, integrity and more, causing job dissatisfaction and burnout, according to a new study from Rice University.

Rice process aims to strip ammonia from wastewater
Engineers develop a high-performance nanowire catalyst that pulls ammonia and solid ammonia (fertilizer) from nitrate in wastewater.

Rice U. students reverse engineer drug-smuggling drone for US Coast Guard
An award-winning team of Rice University engineering students that includes three Rice football players has reverse engineered a robotic drug-smuggling semi-submersible to help the U.S. Coast Guard fight foreign drug cartels.

Study of ancient predators sheds light on how humans did – or didn’t – find food
A new Rice University-led analysis of the remains of ancient predators reveals new information about how prehistoric humans did – or didn’t – find their food.

Automatic admissions policies increased diversity at rural Texas high schools, says report
A Rice University study found “race-blind” automatic admissions policies at Texas’ state universities boosted diversity in highly segregated school districts, especially in rural areas of the Lone Star State.

Houston birdwatcher turned to listening in the pandemic
A Rice geologist’s birding hobby branched out into citizen science during the pandemic.

A new research brief from Rice University’s Kinder Institute for Urban Research has found that English learners have the most success when they stick with a single program — regardless of program type — and skills from their home language are incorporated in their education.

Rice University geobiologist tapped for Antarctic drilling mission
Rice geobiologist Jeanine Ash is participating in an Antarctic mission that’s studying climate change.

Rice trains postdocs for nano-cancer future
The National Institutes of Health extend a grant to help future medical professionals understand nanotechnology-enabled tools to treat cancer.