
Emu stands tall at detecting bacteria species
Rice computer scientists develop Emu, which uses long reads of genomes to identify bacteria in a community.

Emu stands tall at detecting bacteria species
Rice computer scientists develop Emu, which uses long reads of genomes to identify bacteria in a community.

Flooding exacerbates pollution exposure in at-risk urban communities
Increased flooding in the U.S. is exposing more people to industrial pollution, especially in racially marginalized urban communities, according to new research from Rice University, New York University and Brown University.

DOE backs Rice physicists’ collaboration
Rice nuclear physicists win a Department of Energy grant to research the fundamental properties of matter in extreme conditions.
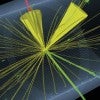
An Owl’s-eye view of the Higgs boson at 10
Anniversary finds Rice physicists pushing forward as Large Hadron Collider reboots

US needs more foreign workers to solve labor crisis, says Baker Institute expert
Allowing more legal immigration and creating a workable solution for the millions of people living in the United States illegally is the only way to effectively address the nation’s worsening labor shortage, according to a report from Rice University’s Baker Institute for Public Policy.

Embryo and embryoid research state regulations are morally inconsistent, say Baker Institute experts
State policies on human embryo and embryoid research are morally inconsistent, according to a paper by Kirstin Matthews and Daniel Moralí published in the Journal of Law and the Biosciences, which reviewed all applicable federal and state laws.

Two experts from the Baker Institute for Public Policy’s Center for Health and Biosciences at Rice University are available to explain the regulatory landscape of human embryo and embryoid research, especially in light of changes to federal policy after Roe v. Wade was overturned.
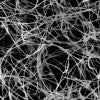
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real
Rice scientists create the first boron nitride nanotube fibers using the custom wet-spinning process they developed to make carbon nanotube fibers.
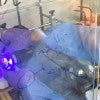
Process to customize molecules does double duty
Chemists develop a method to add two fragments to an alkene molecule in a single process, which could simplify drug and materials design.

Houston’s hot housing market has decreased inventory and widened affordability gap
Houston’s housing market is hotter than ever, people are paying skyrocketing prices for a declining inventory of homes and apartments and the affordability gap is getting worse, according to a new report from Rice University’s Kinder Institute for Urban Research.
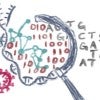
SeqScreen can reveal ‘concerning’ DNA
Rice computer scientists and collaborators develop a program to screen short DNA sequences, whether synthetic or natural, to determine their toxicity.
Agriculture emissions pose risks to health and climate
Rice researchers find the economic cost of emissions from agriculture and their risks to populations through air pollution and climate change.

Rice lab’s quantum simulator delivers new insight
A Rice University quantum simulator is giving physicists a clear look at spin-charge separation, a bizarre phenomenon in which two parts of indivisible particles called electrons travel at different speeds in extremely cold 1D wires. The research is published this week in Science and has implications for quantum computing and electronics with atom-scale wires.

Humans in the loop help robots find their way
Rice computer scientists develop a method that allows humans to help complex robots build efficient solutions to “see” their environments and carry out tasks.

Stressful events can take big toll on those struggling most with death of spouse
Widowed individuals experiencing intense grief after the loss of their spouse experience a significant increase in body inflammation following other stressful events, according to new research from Rice University.