
NIH supports mathematical optimization of tumor treatment
A new strategy to reduce the side effects suffered by patients undergoing treatment for head and neck cancers now has the support of the National Institutes of Health.

NIH supports mathematical optimization of tumor treatment
A new strategy to reduce the side effects suffered by patients undergoing treatment for head and neck cancers now has the support of the National Institutes of Health.

Molecular jiggling has implications for carbon nanotube fibers
New research suggests the jiggling motion of carbon nanotubes suspended in liquid solutions could have implications for the structure, processing and properties of nanotube fibers formed from those solutions.

Moshe Vardi earns top computer science honor
Rice's Moshe Vardi has won the 2021 ACM/AAAI Allen Newell Award for his influential work at the interface of logic and computer science.

World’s largest database on history of slave trade now housed at Rice
SlaveVoyages.org is the result of years of research, reengineered for the future by Rice and a newly formed consortium.

Pristine quantum criticality found
U.S. and Austrian physicists searching for evidence of quantum criticality in topological materials have found one of the most pristine examples yet observed.
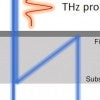
Thin is now in to turn terahertz polarization
Rice lab’s discovery of ‘magic angle’ builds on its ultrathin, highly aligned nanotube films

Body chemistry can predict severity of depression after death of spouse
A new study from researchers at Rice University has found that bodily inflammation after the death of a spouse can predict future depression.

There’s never been a better time to pursue an English degree at Rice
Creative writing program offers unique opportunity to learn from America’s foremost writers and scholars.

Engineered organism could diagnose Crohn's disease flareups
Rice University researchers have engineered a bacterium capable of diagnosing a human disease, a milestone in the field of synthetic biology.

Bio-inspired scaffolds help promote muscle growth
Rice University bioengineers are fabricating and testing tunable electrospun scaffolds completely derived from decellularized skeletal muscle to promote the regeneration of injured skeletal muscle.

Preventing life-threatening pediatric condition starts with pandemic safeguards
HOUSTON – (May 12, 2021) – Adults can be the first line of defense when it comes to avoiding the worst outcomes from multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), a rare but potentially deadly condition linked to COVID-19, according to a new review article from Rice University epidemiologists.

Feds back probe of understudied gut nervous system
Rice University neurobiologist Rosa Uribe has won a five-year, $2 million R01 grant from the National Institutes of Health to study how the enteric nervous system develops.

How planets form controls elements essential for life
How a planet comes together has implications for whether it retains the nitrogen, carbon and water that eventually give rise to life.
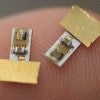
Timing is everything in new implant tech
Rice engineers' wireless implants now allow for multiple stimulators to be programmed and magnetically powered from a single transmitter.

Ostherr’s online database offers a ‘different framing of what an intervention can look like.’