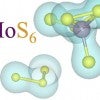
Rice lab peers inside 2D crystal synthesis
Scientific studies describing the most basic processes often have the greatest impact in the long run. A new work by Rice University engineers could be one such, and it’s a gas, gas, gas for nanomaterials.

Rice lab peers inside 2D crystal synthesis
Scientific studies describing the most basic processes often have the greatest impact in the long run. A new work by Rice University engineers could be one such, and it’s a gas, gas, gas for nanomaterials.


Biologists construct a ‘periodic table’ for cell nuclei
A team of biologists studying the tree of life has unveiled a new classification system for cell nuclei, and discovered a method for transmuting one type of cell nucleus into another.

In graphene process, resistance is useful
Lab uses laser-induced graphene process to create micron-scale patterns in photoresist for consumer electronics and more.

Rice names architect for new engineering and science building
With the imminent demolition of Rice University’s Abercrombie Engineering Laboratory, the space will soon be cleared for a new engineering and science building, according to Rice administrators. International architecture firm Skidmore, Owings & Merrill (SOM) has been selected as lead architect for the new building. Houston’s Scientia Architects will consult on laboratory design.
Silver ions hurry up, then wait as they disperse
There’s gold in them thar nanoparticles, and there used to be a lot of silver, too. But much of the silver has leached away, and researchers want to know how.

People, papers and presentations April 12, 2021
Nikhil Gattu, a junior kinesiology and chemistry major, has been named the winner of this year’s Undergraduate Scholar Award by the American Kinesiology Association.

Bioengineer wins NIH grant to attack cystic fibrosis
Rice chemical and biomolecular engineer Xue Sherry Gao wins a National Institutes of Health grant to develop gene editing to treat cystic fibrosis.

Tires turned into graphene that makes stronger concrete
Rice scientists optimize a process to turn rubber from discarded tires into soluble graphene.
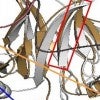
Cancer ‘guardian’ breaks bad with one switch
A mutation that replaces a single amino acid in a potent tumor-suppressing protein makes it prone to nucleating amyloid fibrils implicated in many cancers as well as neurological diseases.

Cerium sidelines silver to make drug precursor
Rice scientists have developed a simplified method to make fluoroketones, a drug precursor that typically requires an expensive silver catalyst.

Theory could accelerate push for spintronic devices
A theory by Rice scientists could boost spintronics, a key to creating faster and more powerful electronic devices, including quantum computers.
DARPA backs Rice sensor to detect COVID-19 virus in air
Researchers receive funding for up to $1 million to develop a real-time electronic sensor able to detect minute amounts of the airborne virus that causes COVID-19 infection.
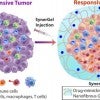
UTHealth, Rice advance oral cancer immunotherapy
Researchers at Rice and the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston develop a hydrogel that could destroy oral cancer tumors.
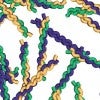
Collagen structures get the royal reveal
An algorithm by Rice University scientists predicts the structures and melting temperatures of collagen, the triple helix that accounts for about a third of the body’s proteins and forms the fibrous glue in skin, bones, muscles, tendons and ligaments.