
Peter Rossky was honored with a symposium Dec. 6-7 at Rice's BioScience Research Collaborative.

Peter Rossky was honored with a symposium Dec. 6-7 at Rice's BioScience Research Collaborative.

Rice’s Technology Development Fund backs faculty projects
Nine projects proposed by Rice researchers have been granted seed funding by Creative Ventures' Technology Development Fund.

People, papers and presentations for Dec. 6, 2021
The Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas has appointed Peter Rodriguez, dean of the Jones Graduate School of Business, to its Houston Branch board of directors, and assistant professor of chemistry Julian West has won a Thieme Chemistry Journals Award for early career synthetic chemists.

Rice profs among historic Greek heroes
Two Rice professors are among physicians and biomedical researchers honored on the Greece bicentennial.

People, papers and presentations for Nov. 22, 2021
People, papers and presentations for Nov. 22, 2021

Rice lab first to mimic molecule found in poppies
A Rice undergraduate leads the discovery of a way to synthesize a rare molecule drawn from poppies.

Rice strategy refines genetic base editors
A new strategy by Rice University scientists seeks to avoid gene-editing errors by fine-tuning specific CRISPR-base editing parameters in advance.

Rice tapped to develop 3D-printed ‘smart helmets’ for the military
Rice University researchers have embarked upon a project to build the first printable “smart helmet” with funding from the Department of Defense.

Nicolaou wins Robert Koch Gold Medal
K.C. Nicolaou, the Harry C. and Olga K. Wiess Professor of Chemistry, has been awarded the Robert Koch Gold Medal for his life’s work in biomedical science.
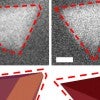
This pyramid scheme could be helpful
Rice chemists uncover the mechanism behind controlled growth of gold tetrahedron nanoparticles using liquid cell transmission electron microscopy.

Manganese makes its mark in drug synthesis
Rice University chemists find manganese far superior to silver and cerium as a way to make building blocks for drug design and manufacture.

Urban mining for metals flashes electronic trash into treasure
Flash Joule heating recovers valuable and toxic metals from electronic waste. The process allows for “urban mining” of resources that could be a win for the environment as well as for manufacturers.

Corps of Engineers funds bid to ‘flash’ waste into useful materials
A $5.2 million U.S. Army Corps of Engineers grant will expand Rice efforts to recycle waste into valuable products through flash Joule heating.

American Chemical Society honors Gustavo Scuseria
Rice University’s Gustavo Scuseria wins the American Chemical Society Award in Theoretical Chemistry.
NSF extends Physics of Living Systems network at Rice
The NSF awards nearly $3 million to the Center for Theoretical Biological Physics to continue its leadership role in the Physics of Living Systems graduate research network.