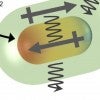
‘Soft’ nanoparticles give plasmons new potential
Bigger is not always better, but here’s something that starts small and gets better as it gets bigger.

‘Soft’ nanoparticles give plasmons new potential
Bigger is not always better, but here’s something that starts small and gets better as it gets bigger.
Light flips genetic switch in bacteria inside transparent worms
Researchers from Rice University and Baylor College of Medicine have shown that colored light can both activate and deactivate genes of gut bacteria in the intestines of worms. The research shows how optogenetic technology can be used to investigate the health impacts of gut bacteria.

AI-powered microscope could check cancer margins in minutes
Researchers from Rice University and MD Anderson Cancer Center have created a microscope that uses artificial intelligence to quickly and inexpensively image large tissue sections at high resolution with minimal preparation. If clinically validated, the DeepDOF microscope could allow surgeons to inspect tumor margins within minutes.
Antibody study suggests COVID-19 infections underestimated
A monthslong study to determine the number of Houstonians carrying COVID-19 antibodies revealed infections may have been four times greater than viral tests showed, according to collaborators at the Houston Health Department, Rice University and Baylor College of Medicine.

State of the University: President hails 'remarkable performance'
David Leebron delivered his 2020 State of the University address with a salute to the university’s faculty, staff and students for overcoming the year’s unprecedented challenges.

Bad news for fake news: Rice research helps combat social media misinformation
Improved use of machine learning can double throughput of real-time information filters, Rice researchers find.
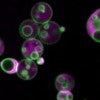
Hidden structure found in essential metabolic machinery
Rice University biochemists have discovered membrane-divided subcompartments within organelles called peroxisomes, essential pieces of metabolic machinery for all higher order life from yeast to humans. The research appears this week in Nature Communications.

Rice physicist shares grant to advance imaging
The lab of physicist Junichiro Kono will share in a $1 million grant from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative to improve imaging of proteins, cells and tissues.

Rice scientist joins next Mars adventure
A Rice University geologist is one of 13 scientists recently selected to operate the Mars rover Perseverance and analyze samples for an eventual return to Earth.

'Strategic indifference' leaves refugees in precarious position, says Baker Institute expert
Current explanations for migrant and refugee policies in the "global south" mistake the absence of formal policy for neglect. But a migration and immigration expert at Rice's Baker Institute for Public Policy proposes to explain this dynamic as "strategic indifference.”

AI helps scientists understand brain activity behind thoughts
Researchers from Baylor College of Medicine and Rice University have developed artificial intelligence models that help them better understand the brain computations that underlie thoughts.
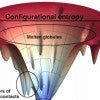
Understanding frustration could lead to better drugs
Atom-scale models of proteins that incorporate ligands, like drug molecules, show a strong correlation between minimally frustrated binding sites and drug specificity. Such models could lead to better-designed drugs with fewer side effects.

Voter research amid pandemic wins Rice students new national award
Undergrad team wowed judges by helping secure millions for polling place safety across Harris County.
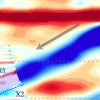
Former piece of Pacific Ocean floor imaged deep beneath China
In a study that gives new meaning to the term "rock bottom," seismic researchers have discovered the underside of a rocky slab of Earth's lithosphere that has been pulled more than 400 miles beneath northeastern China by the process of tectonic subduction.