
Graphene gets enhanced by flashing
Rice University scientists who developed the flash Joule heating process to make graphene have found a way to produce doped graphene to customize it for applications.

Graphene gets enhanced by flashing
Rice University scientists who developed the flash Joule heating process to make graphene have found a way to produce doped graphene to customize it for applications.

US News grad school rankings give high marks to Rice programs
A total of 19 graduate programs at Rice University rank among the nation's top 25 in their categories in the latest edition of U.S. News and World Report’s “Best Graduate Schools.”

Closer look helps Rice lab ponder when a protein’s prone to wander
Rice chemists have discovered surface interactions could be tunable at the single-protein level

Faculty set Rice record with eight CAREER Awards
Rice faculty set a record, winning eight NSF CAREER Awards in 2002

Army touts Rice contribution to graphene collaboration
Rice's graphene research is making its presence felt in the U.S. Army’s work to develop applications using the single-atom-thick form of carbon.

Environmental champions win Rice grants
The Rice University Sustainable Futures Fund backs six projects to help bolster the planet’s environmental health.

Rare earth elements await in waste
Rice University scientists applied their flash Joule heating process to coal fly ash and other toxic waste to safely extract rare earth elements essential to modern electronics and green technologies.

Matthew Jones wins NSF CAREER Award
Rice chemist Matthew Jones wins an NSF CAREER Award to study controlled growth of metallic nanoparticles for biomedicine, energy storage and computing.

Machine learning fine-tunes flash graphene
Rice University scientists are using machine learning techniques to streamline the process of synthesizing graphene from waste through flash Joule heating.

Now you don’t see it … and now you do
Scientists and engineers from Rice University and the Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research discover fluorescence from silicon nanoparticles in cement and show how it can be used to reveal early signs of damage in concrete structures.
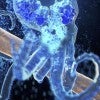
Antibody with engineered peptide targets bone metastasis
A moderate amount of a peptide-enhanced cancer drug goes a long way in treating breast cancers that metastasize to the bone.

When graphene speaks, scientists can now listen
Brothers working in a lab at Rice University discover that sound can be used to analyze the properties of laser-induced graphene in real time.

People, papers and presentations for Jan. 18, 2022
Rice chemist James Tour is among 32 investigators in five countries who will collaborate on the “Mend the Gap!” project to heal spinal cord injuries.
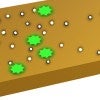
Migrating holes help catalysts be productive
A theoretical model suggests electron holes that propagate at active sites on a catalyst migrate, triggering other sites that continue the process.

Quirky kveik’s yeasty questions no match for freshmen chemistry students
How Carrie McNeil’s Introduction to Scientific Research Challenges course helped a Houston brewery solve a salty problem