
Trailblazing Rice bioengineer is turning cells into disease fighters
Rice University bioengineer Isaac Hilton has been awarded an NIH Trailblazer Award to create synthetic circular DNA that can be used to reprogram cells as disease fighters.

Trailblazing Rice bioengineer is turning cells into disease fighters
Rice University bioengineer Isaac Hilton has been awarded an NIH Trailblazer Award to create synthetic circular DNA that can be used to reprogram cells as disease fighters.
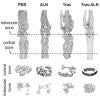
Rice, Baylor win defense grant to advance metastasis study
Rice University chemist Han Xiao and biologist Xiang Zhang at Baylor College of Medicine have won a $2.3 million Department of Defense grant to expand their efforts to halt bone cancer metastasis.

When many act as one, data-driven models can reveal key behaviors
Data science approaches can reveal subtle clues about the origins of such collective behaviors as aggregation of bacteria.

Rep. Dan Crenshaw hosts health care summit, tours neuroengineering labs
U.S. Rep. Dan Crenshaw (left), R-Texas, hosted his third annual Healthcare Innovation Summit July 23 at Rice University's BioScience Research Collaborative (BRC) in conjunction with the university's Institute of Biosciences and Bioengineering.
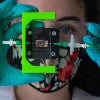
Rice team creating insulin-producing implant for Type 1 diabetes
Rice University bioengineers are using 3D printing and smart biomaterials to create an insulin-producing implant for Type 1 diabetics.
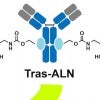
Drug doubles down on bone cancer, metastasis
Researchers at Rice University and Baylor College of Medicine develop an antibody conjugate called BonTarg that delivers drugs to bone tumors and inhibits metastasis.

Six Rice-TMC research teams earn seed grants
Rice's Educational and Research Initiatives for Collaborative Health has announced six seed grants for research collaborations between faculty from Rice and the Texas Medical Center.
Keck backs Rice bid to ‘build a brain’
A $1 million Keck Foundation grant will support work by Jacob Robinson to understand neural pathways.

RAMBO speeds searches on huge DNA databases
Rice computer scientists are sending RAMBO to rescue genomic researchers who sometimes wait days or weeks for search results from enormous DNA databases.

Study examines how breast implant surfaces affect immune response
Rice University bioengineers collaborated on a six-year study that systematically analyzed how the surface architecture of silicone breast implants influences adverse side effects.

NIH supports mathematical optimization of tumor treatment
A new strategy to reduce the side effects suffered by patients undergoing treatment for head and neck cancers now has the support of the National Institutes of Health.
Bacteria have sensors to shut toxin down
Researchers at Rice University and the University of Idaho helped identify a protein that senses and binds to formaldehyde to tell cells that toxic formaldehyde is building up.

Engineered organism could diagnose Crohn's disease flareups
Rice University researchers have engineered a bacterium capable of diagnosing a human disease, a milestone in the field of synthetic biology.

Feds back probe of understudied gut nervous system
Rice University neurobiologist Rosa Uribe has won a five-year, $2 million R01 grant from the National Institutes of Health to study how the enteric nervous system develops.

Wearable glucose monitors shed light on progression of Type 2 diabetes in Hispanic/Latino adults
In one of the first studies of its kind, medical and engineering researchers have shown wearable devices that continuously monitor blood sugar provide new insights into the progression of Type 2 diabetes among at-risk Hispanic/Latino adults.