
Rice physicist Pengcheng Dai wins superconductivity award
Rice University physicist Pengcheng Dai and two European physicists have won the 2022 Heike Kamerlingh Onnes Prize, one of the leading awards for experimental research in superconductivity.

Rice physicist Pengcheng Dai wins superconductivity award
Rice University physicist Pengcheng Dai and two European physicists have won the 2022 Heike Kamerlingh Onnes Prize, one of the leading awards for experimental research in superconductivity.

NSF funds Rice effort to measure, preserve quantum entanglement
Rice University physicist Guido Pagano has won a prestigious CAREER award from the National Science Foundation (NSF) to study quantum entanglement and develop new error-correcting tools for quantum computation.
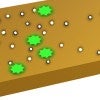
Migrating holes help catalysts be productive
A theoretical model suggests electron holes that propagate at active sites on a catalyst migrate, triggering other sites that continue the process.
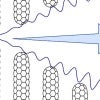
Nanotube fibers stand strong -- but for how long?
A Rice University study calculates how cyclic strain and stress affects nanotubes and describes how fibers under cyclic loads can fail over time.

A-list candidate for fault-free quantum computing delivers surprise
Superconducting uranium ditelluride is a promising material in the race to create fault-tolerant quantum computers, but physicists are rethinking how superconductivity arises in the material in light of puzzling new experimental evidence in this week’s issue of Nature.
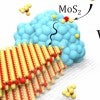
Nickel’s need for speed makes unusual nanoribbons
It’s now possible to quickly make ultrathin nanoribbons of molybdenum disulfide, with a speedy nickel nanoparticle leading the way.

Ultrathin solar cells get a boost
Rice University engineers boost the efficiency while retaining the toughness of solar cells made of two-dimensional perovskites.
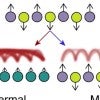
Rice prof’s Nature paper details unique quantum phenomenon
Rice physicist Guido Pagano is part of a team reporting in Nature on the discovery of a new phenomenon in quantum systems.
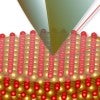
Magnetene’s ultra-low friction explained
Rice scientists help make the first measurements of ultra-low friction in 2D magnetene.
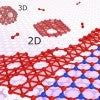
Weak bonds a strength in making borophene
Rice University researchers show how borophene, the 2D form of boron, can be grown to simplify its use for applications.

American Chemical Society honors Gustavo Scuseria
Rice University’s Gustavo Scuseria wins the American Chemical Society Award in Theoretical Chemistry.

Message from provost on launch of Rice Quantum Initiative
For more than four decades, Rice University scientists and engineers have explored and expanded the boundaries of quantum science and created revolutionary computation, sensing and communication technologies based on the principles of quantum mechanics.

Rice physicists find 'magnon' origins in 2D magnet
Rice physicists have confirmed the topological origins of magnons, magnetic features they discovered three years ago in a 2D material that could prove useful for spintronics.
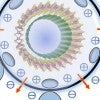
Double-walled nanotubes have electro-optical advantages
Rice theorists find that flexoelectric effects in double-walled carbon nanotubes could be highly useful for photovoltaic applications.

Scientists make bilayer borophene for the first time. The versatile 2D material shows promise for quantum electronics, energy storage and sensors.