
Rice’s Technology Development Fund backs faculty projects
Nine projects proposed by Rice researchers have been granted seed funding by Creative Ventures' Technology Development Fund.

Rice’s Technology Development Fund backs faculty projects
Nine projects proposed by Rice researchers have been granted seed funding by Creative Ventures' Technology Development Fund.
NSF grant supports study of cells’ early decisions
Rice University receives National Science Foundation support to build a model of cell differentiation during the earliest stage of life. The model could help improve researchers’ ability to direct stem cells to a given fate.

Microplastic pollution aids antibiotic resistance
Microplastics dispersed in the environment may enhance antibiotic resistance. A study led by Rice University found the chemical-leaching plastics draw bacteria and other vectors and make them susceptible to antibiotic resistant genes.
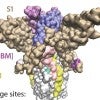
Omicron mutations may help SARS-CoV-2 evade antibodies
Software under development at Rice University and its partners reveals mutations in the omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 that may help it evade antibodies, including those from vaccinations.

Rice conference on natural disasters draws international panelists, attendees
The Nov. 19-20 conference focused on narratives around natural catastrophes in the Americas and Circum-Caribbean

‘Bound Away’ conference bringing new research on slave voyages
Art exhibitions at Moody, MFAH will contextualize research presented Dec. 3-4

Ultrathin solar cells get a boost
Rice University engineers boost the efficiency while retaining the toughness of solar cells made of two-dimensional perovskites.
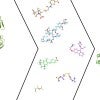
Rice web server helps identify COVID-19 drug candidates
Rice University engineers are leading the development of a web server to help researchers judge the efficacy of their COVID-19 treatment candidates.

Anticorrosion coating sets new benchmark
Rice engineers adapt a compound to serve as a universal anticorrosive coating for steel.

Nanoscale lattices flow from 3D printer
Rice University engineers are printing 3D lattices of glass and crystal with sub-200 nanometer resolution. The technique could make it practical to print micro-scale electronic, mechanical and photonic devices.

Manganese makes its mark in drug synthesis
Rice University chemists find manganese far superior to silver and cerium as a way to make building blocks for drug design and manufacture.

Corps of Engineers funds bid to ‘flash’ waste into useful materials
A $5.2 million U.S. Army Corps of Engineers grant will expand Rice efforts to recycle waste into valuable products through flash Joule heating.
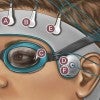
US Army backs ‘sleeping cap’ to help brains take out the trash
Rice engineers are developing a noninvasive device to understand how the brain disposes of metabolic waste during sleep.

A loose-fitting mask may be doing you no favors if you’re around SARS-CoV-2.
Sex and the symbiont: Can algae hookups help corals survive?
Scientists have discovered that symbiotic single-celled algae that live inside of and feed corals can reproduce not only by mitosis, but also sexually. Encouraging sex in these algae can accelerate their evolution to produce strains better able to help reefs cope with climate change.