
New CPRIT chemistry professor to enhance cancer research at Rice
Rice’s Department of Chemistry will soon welcome Professor David Sarlah.

New CPRIT chemistry professor to enhance cancer research at Rice
Rice’s Department of Chemistry will soon welcome Professor David Sarlah.

Rice and Houston Community College collaborate to diversify access to biomedical research training
Rice and Houston Community College collaborate to diversify access to biomedical research training through program funded by a $1.8M NIH grant.

Rice chemist Gustavo Scuseria wins 2024 Schrödinger Medal
Pioneering Rice chemist Gustavo Scuseria has won the 2024 Schrödinger Medal from the World Association of Theoretical and Computational Chemists.

Chemist Julian West makes C&EN magazine’s ‘Talented 12’ list
Rice University chemist Julian West is one of a dozen up-and-coming young scientists featured in Chemical & Engineering News’ (C&EN) 2024 Talented 12, an annual issue of the weekly news magazine that highlights rising stars across all chemistry research disciplines.

Rice study reveals insights into protein evolution
Rice University’s Peter Wolynes and his research team have unveiled a breakthrough in understanding how specific genetic sequences, known as pseudogenes, evolve. Their paper was published May 13 by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America Journal.


Researchers at Rice University have successfully synthesized a group of natural compounds known as fusicoccanes. The molecules, found in various living organisms, exhibit diverse biological activities, including the ability to modulate protein-protein interactions within biological systems.
Aligned peptide ‘noodles’ could enable lab-grown biological tissues
A team of Rice researchers and collaborators have developed peptide-based hydrogels that mimic the aligned structure of muscle and nerve tissues, which could enable the development of functional lab-grown tissue.

Faculty, staff, students honored for excellence in teaching, mentoring, service
Each year, Rice honors members of the university community who have served students through outstanding teaching, dedication and service.

Rice alumna wins prestigious merit-based fellowship for new Americans
Rice University alumna Minjung Kim is one of 30 recipients of the Paul & Daisy Soros Fellowships for New Americans, a merit-based graduate school program for immigrants and children of immigrants.

Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes
A team of researchers from Rice University and the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign has shown that molecules can be as formidable at scrambling quantum information as black holes by combining mathematical tools from black hole physics and chemical physics and testing their theory in chemical reactions.

Rice Emerging Scholars Program receives $2.5M NSF grant to boost STEM education
Rice University’s Emerging Scholars Program (RESP) has received a five-year, $2.5 million grant from the National Science Foundation. The funding aims to bolster achievements in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) among students from under-resourced families and communities.

Rice’s new Synthesis X Center has winning formula for cancer innovation
Rice has created the new Synthesis X Center to bring together clinicians treating cancer and researchers looking for cures to help spur drug discovery make precision adjustments to drug properties and translate fundamental research discoveries into clinical applications.

Rice’s Naomi Halas awarded Optica’s C.E.K. Mees Medal
Rice University’s Naomi Halas has been selected as the 2024 recipient of the C.E.K. Mees Medal by Optica for her “original use of optics across multiple fields.”
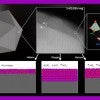
Aluminum nanoparticles make tunable green catalysts
The Rice lab of nanotechnology pioneer Naomi Halas has uncovered a transformative approach to harnessing the catalytic power of aluminum nanoparticles by annealing them in various gas atmospheres at high temperatures.