
Rice graduate students awarded NSF INTERN grants for real-world research opportunities
Rice graduate students Eric Wuesthoff and Esther Jimenez are the recipients of the National Science Foundation’s INTERN awards.

Rice graduate students awarded NSF INTERN grants for real-world research opportunities
Rice graduate students Eric Wuesthoff and Esther Jimenez are the recipients of the National Science Foundation’s INTERN awards.
Researchers teaching artificial intelligence about frustration in protein folding
Peter Wolynes and his colleagues have found a new way to predict how proteins change their shape when they function.
Researchers make breakthrough in fight against COVID-19
Jose Onuchic is part of a research team that has made a discovery in the fight against SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19.

New twist on synthesis technique developed at Rice promises sustainable manufacturing
James Tour’s lab at Rice has developed a new method known as flash-within-flash Joule heating.

Rice-built reactor yields green ammonia and purified water
Rice engineers have developed a revolutionary reactor design that could decarbonize ammonia production while also mitigating water pollution.

Angel Martí elected fellow of the American Chemical Society
Rice’s Angel Martí has been elected a fellow of the American Chemical Society, one of his discipline’s highest honors.

Rice is top destination for Mexican students who receive Fulbright awards
Seven master’s and Ph.D. Fulbright recipients from Mexico will study at Rice this fall, the most of any university and nearly double the number of any other university, including Rice’s Association of American Universities peers.

New $12M research project aims to provide ‘practical solutions to critical environmental challenges’
Scientists at Rice, in collaboration with the U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center, are making headway in addressing per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) contamination.

Rice researchers develop innovative battery recycling method
A research team at Rice led by James Tour is tackling the environmental issue of efficiently recycling lithium ion batteries amid their increasing use.

Rice chemist James Tour has led a research team to develop a rapid electrothermal mineralization process, which in seconds can remediate the accumulation of synthetic chemicals that can contaminate soil and the environment.
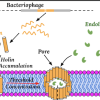
Rice researchers unveil secrets behind viral precision
New research from Rice scientists is shedding light on how viruses ensure their survival by precisely timing the release of new viruses.
Researchers discover ancient chromosomes in 52,000-year-old woolly mammoth
Researchers have discovered fossils of ancient chromosomes preserved in the remains of a woolly mammoth that died 52,000 years ago.

Rice researchers uncover key mechanisms in chromosome structure development
Researchers at Rice are making strides in understanding how chromosome structures change throughout the cell’s life cycle.

Rice research aims to reprogram the genetic code
Chemist Han Xiao has been awarded nearly $2 million from the National Institutes of Health Maximizing Investigators’ Research Award.

Do genes-in-pieces code for proteins that fold in pieces?
A new study led by Peter Wolynes offers new insights into the evolution of foldable proteins.