Odds are good for unique 2D compound
Rice University engineers make 2D materials for valleytronics, a platform for information processing and storage that relies on the manipulation of electrons’ positions in energetic “valleys.”

Odds are good for unique 2D compound
Rice University engineers make 2D materials for valleytronics, a platform for information processing and storage that relies on the manipulation of electrons’ positions in energetic “valleys.”
Targeted tumors attack not-innocent bystanders
Antibody-drug conjugates developed are found to attack not only targeted tumor cells but also nontargeted “bystanders.”
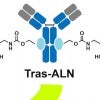
Drug doubles down on bone cancer, metastasis
Researchers at Rice University and Baylor College of Medicine develop an antibody conjugate called BonTarg that delivers drugs to bone tumors and inhibits metastasis.
Rice, Rutgers developing inhalable COVID-19 vaccine spray
Scientists at Rice and Rutgers developing two COVID-19 vaccine strategies that do not require cold storage, one of which can be inhaled.

NIH grant will help streamline chemical synthesis
Rice University chemist Julian West has won a five-year, $1.8 million National Institutes of Health grant to advance his lab’s efforts to simplify the synthesis of organic chemicals.
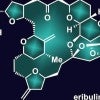
Reversal speeds creation of important molecule
A Rice lab’s reverse approach to making halichondrin B is the shortest route to a “rather complex and important molecule."

Nightside radio could help reveal exoplanet details
Rice scientists enhance models that could be used to detect magnetosphere activity on exoplanets. The Rice model adds data from nightside activity that could increase signals by at least an order of magnitude.

Lillian Wieland’s freshman-year presentation for the Rice Undergraduate Research Symposium (RURS) “went terribly,” as she recalls it.

Rice welcomes teachers for in-person physics workshop
QuarkNet returned to Rice last week for the first in-person workshop on campus since the start of the pandemic.
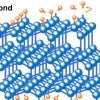
‘Flashed’ nanodiamonds are just a phase
The “flash” process developed at Rice University can turn carbon black into functionalized nanodiamond and other materials. The carbon atoms evolved through several phases depending on the length of the flash.

Odd angles make for strong spin-spin coupling
HOUSTON – (May 25, 2021) – Sometimes things are a little out of whack, and it turns out to be exactly what you need.

Seismic study will help keep carbon underground
A Department of Energy grant to Rice geoscientists enables development of fiber-optic sensors to find and evaluate small faults at underground carbon dioxide storage reservoirs.

A recently arrived Rice University professor preparing to study quantum systems assembled from the ground up with individual atoms has two significant papers on which to build his reputation.

f identical versions of 20 people lived out their lives in dozens of different worlds, would the same people be popular in each world?

Biologists construct a ‘periodic table’ for cell nuclei
A team of biologists studying the tree of life has unveiled a new classification system for cell nuclei, and discovered a method for transmuting one type of cell nucleus into another.