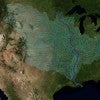
NSF backs study of Mississippi River’s response to climate change
Rice climate scientists and engineers are studying how climate change will impact Mississippi River flooding.

NSF backs study of Mississippi River’s response to climate change
Rice climate scientists and engineers are studying how climate change will impact Mississippi River flooding.

Graphene gets enhanced by flashing
Rice University scientists who developed the flash Joule heating process to make graphene have found a way to produce doped graphene to customize it for applications.

Adrienne Correa wins CAREER Award
Rice marine biologist Adrienne Correa has won a prestigious CAREER Award from the National Science Foundation.

A ‘quasi-juvenile delinquent’ at Rice rises to the top -- again
Rice University alumnus Dennis Sullivan wins the Abel Prize in Mathematics.

Run not just fun for Rice students, elementary partners
Getting out and mentoring elementary students in physical fitness turns out to be just as beneficial for college students, Rice University study finds.

Saudi Aramco joins Rice University’s Carbon Hub
Saudi Aramco joins Rice’s Carbon Hub research initiative to accelerate the energy transition by developing sustainable uses of hydrocarbons.

Rice, Houston Methodist launch Center for Human Performance
Rice and Houston Methodist are creating a center to advance research and education in human performance.

Closer look helps Rice lab ponder when a protein’s prone to wander
Rice chemists have discovered surface interactions could be tunable at the single-protein level

Faculty set Rice record with eight CAREER Awards
Rice faculty set a record, winning eight NSF CAREER Awards in 2002

Voyage reveals wonder and beauty of ‘long-dead ocean dwellers’
Rice Ph.D. student Debadrita Jana is part of a scientific voyage exploring deep beneath the Indian Ocean.
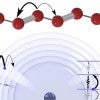
Physicists harness electrons to make ‘synthetic dimensions’
Rice University physicists have learned to manipulate electrons in gigantic Rydberg atoms with such precision they can create “synthetic dimensions” where the system acts as if it had extra spatial dimensions, which are important tools for quantum simulations.

Inaugural class of Rice Innovation Fellows announced
The Provost’s Office and the Liu Idea Lab for Innovation & Entrepreneurship (Lilie) have announced the inaugural class of Rice Innovation Fellows, a program that will provide educational and financial support to the next generation of scientist- and engineer-led spinout ventures.

Environmental champions win Rice grants
The Rice University Sustainable Futures Fund backs six projects to help bolster the planet’s environmental health.

Strong magnets put new twist on phonons
Phonons, quasiparticles in a crystal lattice that are usually hard to control by external fields, can be manipulated by a magnetic field -- but it takes a very strong magnet.

Bacterial ‘bully’ could improve food production
Lactic acid bacteria that thrive in many organisms, including humans, employ a hybrid metabolism that combines respiration and fermentation to give it an advantage over competitors. Researchers say the discovery could lead to enhanced techniques for food and chemical production.