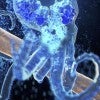
Antibody with engineered peptide targets bone metastasis
A moderate amount of a peptide-enhanced cancer drug goes a long way in treating breast cancers that metastasize to the bone.

Antibody with engineered peptide targets bone metastasis
A moderate amount of a peptide-enhanced cancer drug goes a long way in treating breast cancers that metastasize to the bone.

When graphene speaks, scientists can now listen
Brothers working in a lab at Rice University discover that sound can be used to analyze the properties of laser-induced graphene in real time.

Halting antibiotic resistance is a little less futile
Rice University bioscientists develop a microfluidic platform for high-throughput studies of how bacteria evolve antibiotic resistance.
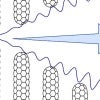
Nanotube fibers stand strong -- but for how long?
A Rice University study calculates how cyclic strain and stress affects nanotubes and describes how fibers under cyclic loads can fail over time.

Ultrathin solar cells get a boost
Rice University engineers boost the efficiency while retaining the toughness of solar cells made of two-dimensional perovskites.
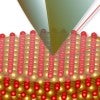
Magnetene’s ultra-low friction explained
Rice scientists help make the first measurements of ultra-low friction in 2D magnetene.

Rice tapped to develop 3D-printed ‘smart helmets’ for the military
Rice University researchers have embarked upon a project to build the first printable “smart helmet” with funding from the Department of Defense.

Urban mining for metals flashes electronic trash into treasure
Flash Joule heating recovers valuable and toxic metals from electronic waste. The process allows for “urban mining” of resources that could be a win for the environment as well as for manufacturers.

Corps of Engineers funds bid to ‘flash’ waste into useful materials
A $5.2 million U.S. Army Corps of Engineers grant will expand Rice efforts to recycle waste into valuable products through flash Joule heating.
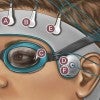
US Army backs ‘sleeping cap’ to help brains take out the trash
Rice engineers are developing a noninvasive device to understand how the brain disposes of metabolic waste during sleep.
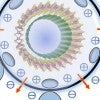
Double-walled nanotubes have electro-optical advantages
Rice theorists find that flexoelectric effects in double-walled carbon nanotubes could be highly useful for photovoltaic applications.

Scientists make bilayer borophene for the first time. The versatile 2D material shows promise for quantum electronics, energy storage and sensors.
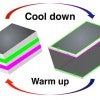
Physicists find room-temperature, 2D-to-1D topological transition
Physicists have discovered a room-temperature transition between 1D and 2D electrical conduction states in the topological insulator bismuth iodide.
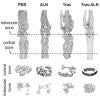
Rice, Baylor win defense grant to advance metastasis study
Rice University chemist Han Xiao and biologist Xiang Zhang at Baylor College of Medicine have won a $2.3 million Department of Defense grant to expand their efforts to halt bone cancer metastasis.

Woven nanotube fibers turn heat into power
Carbon nanotubes woven into thread-like fibers and sewn into fabrics become a thermoelectric generator that can turn heat from the sun or other sources into energy.