Drug doubles down on bone cancer, metastasis
Researchers at Rice University and Baylor College of Medicine develop an antibody conjugate called BonTarg that delivers drugs to bone tumors and inhibits metastasis.

Drug doubles down on bone cancer, metastasis
Researchers at Rice University and Baylor College of Medicine develop an antibody conjugate called BonTarg that delivers drugs to bone tumors and inhibits metastasis.

Solar energy collectors grown from seeds
Rice University engineers have created microscopic seeds for growing remarkably uniform 2D perovskite crystals that are both stable and highly efficient at harvesting electricity from sunlight.
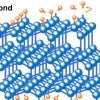
‘Flashed’ nanodiamonds are just a phase
The “flash” process developed at Rice University can turn carbon black into functionalized nanodiamond and other materials. The carbon atoms evolved through several phases depending on the length of the flash.

Odd angles make for strong spin-spin coupling
HOUSTON – (May 25, 2021) – Sometimes things are a little out of whack, and it turns out to be exactly what you need.

Absorbent aerogels show some muscle
A simple chemical process developed at Rice University creates light and highly absorbent aerogels that can take a beating.

In graphene process, resistance is useful
Lab uses laser-induced graphene process to create micron-scale patterns in photoresist for consumer electronics and more.
Silver ions hurry up, then wait as they disperse
There’s gold in them thar nanoparticles, and there used to be a lot of silver, too. But much of the silver has leached away, and researchers want to know how.

Rice, Intel optimize AI training for commodity hardware
New AI software trains deep neural networks 15 times faster than platforms based on graphics processors.

Tires turned into graphene that makes stronger concrete
Rice scientists optimize a process to turn rubber from discarded tires into soluble graphene.

Bottling the world's coldest plasma
Rice University physicists have discovered a way to trap the world's coldest plasma in a magnetic bottle, a technological achievement that could advance research into clean energy, space weather and astrophysics.

Bioinformatics tool accurately tracks synthetic DNA
A Rice computer science lab challenges -- and beats -- deep learning in a test to see if a new bioinformatics approach effectively tracks the lab of origin of a synthetic genetic sequence.

Theory could accelerate push for spintronic devices
A theory by Rice scientists could boost spintronics, a key to creating faster and more powerful electronic devices, including quantum computers.
DARPA backs Rice sensor to detect COVID-19 virus in air
Researchers receive funding for up to $1 million to develop a real-time electronic sensor able to detect minute amounts of the airborne virus that causes COVID-19 infection.
‘Defective’ carbon simplifies hydrogen peroxide production
Rice scientists introduce a new catalyst to reduce oxygen to widely used hydrogen peroxide.

Research could dramatically lower cost of electron sources
Rice University engineers have discovered technology that could slash the cost of semiconductor electron sources, key components in devices ranging from night-vision goggles and low-light cameras to electron microscopes and particle accelerators.