Eco-efficient cement could pave the way to a greener future
Rice U. scientists develop process to remove toxic heavy metals from coal fly ash, making for greener, stronger concrete.

Eco-efficient cement could pave the way to a greener future
Rice U. scientists develop process to remove toxic heavy metals from coal fly ash, making for greener, stronger concrete.
Potential for profits gives Rice lab’s plastic waste project promise
Rice University scientists create carbon nanotubes and other hybrid nanomaterials out of plastic waste using an energy-efficient, low-cost, low-emissions process that could also be profitable.

Climate warming reduces organic carbon burial beneath oceans
A first-of-its-kind study suggests climate warming could reduce organic carbon burial and increase the amount of carbon that’s returned to the atmosphere.

Rice lab’s catalyst could be key for hydrogen economy
A light-activated catalyst efficiently converts ammonia into clean-burning hydrogen using only inexpensive raw materials.

Rice turns asphaltene into graphene for composites
The flash Joule heating process developed at Rice turns asphaltenes, a byproduct of crude oil production, into graphene for use in composite materials.

Rice U. technology startup Syzygy Plasmonics raises $76 million in latest funding round
Syzygy Plasmonics, a Houston-based startup fueled by technology developed at Rice University, has announced $76 million in Series C financing led by Carbon Direct Capital — one of the largest rounds of funding for a venture spun out of a Rice lab.

Drought in China could devastate global supply chains, energy transition efforts, experts warn
Following a record-breaking drought over the summer, China is on the brink of a water catastrophe that could have devastating consequences for global food security, energy markets and supply chains, according to a report from Rice University’s Baker Institute for Public Policy.

TEDxRiceU Countdown to focus on ideas, solutions to climate change
Combating climate change will be the subject of featured speakers sharing their ideas from 5-8 p.m., Nov. 12 at Rice University’s Moody Center for the Arts.
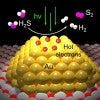
New catalyst can turn smelly hydrogen sulfide into a cash cow
Rice engineers and scientists and collaborators have discovered an efficient, one-step process for converting hydrogen sulfide gas into clean-burning hydrogen fuel.

Rice lab advances water-splitting catalysts
Rice University engineers have developed a stable water-splitting catalyst for clean hydrogen generation that could potentially replace expensive iridium catalysts.

Climate change will create more refugees and necessitate new legal protections, say experts
The international community must prepare for “climate change refugees” — displaced either within their home countries or across borders — experts from Rice University’s Baker Institute for Public Policy argue in a new report.

Halas, Nordlander honored in Rome
Italian President Sergio Mattarella presented Rice’s Naomi Halas and Peter Nordlander the 2022 Eni Energy Transition Award in an Oct. 3 ceremony in Rome's Quirinal Palace.

Climate risks for Gulf of Mexico coral reefs spelled out in study
Promptly reducing greenhouse emissions would give Gulf of Mexico corals up to 20 extra years to adapt to critical threshold temperatures, according to Rice research.

Can fungi help Texas’ grasses cope with climate change?
Rice biologists are using Texas as a living lab to study how symbiotic fungi help grasses tolerate drought.

Halas, Nordlander win prestigious Eni Energy Transition Award
Rice’s Naomi Halas and Peter Nordlander have won the prestigious 2022 Eni Energy Transition Award.