Molecular machines could treat fungal infections
Rice scientists show that light-activated nanoscale drills can kill pathogenic fungi.

Molecular machines could treat fungal infections
Rice scientists show that light-activated nanoscale drills can kill pathogenic fungi.

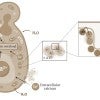
Rice lab uncovers dynamics behind protein crucial in breast cancer
Just as a puppeteer moves a puppet by manipulating its strings, estrogen receptors, which play a crucial role in breast cancer, work in similar ways when they facilitate the interaction between hormones and DNA, according to Rice scientists.

Rice scientists’ discovery could lead to new Alzheimer’s therapies
A new approach to the study of amyloid-beta, a peptide associated with Alzheimer’s disease, has led Rice University scientists to findings that could have a significant impact on the understanding and potential treatment of the disease.

Naomi Halas named University Professor
Rice University has promoted nanotechnology pioneer Naomi Halas to its highest academic rank, University Professor. Halas, a 33-year member of Rice’s faculty, becomes only the 10th person and second woman to earn the title in Rice’s 111-year history.

New enzyme could mean better drugs
Biomolecular engineers at Rice University identified a new enzyme that catalyzes the Nobel Prize-winning Diels-Alder reaction.

Nanoparticles make it easier to turn light into solvated electrons
Chemists from Rice, UT Austin and Stanford have uncovered the long-sought mechanism of a light-driven process that creates solvated electrons, inherently clean chemical reactants that are attractive for green chemistry.
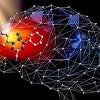
New fluorescent dye can light up the brain
Rice chemist Han Xiao and Stanford researcher Zhen Cheng have developed a tool for noninvasive brain imaging that can help illuminate hard-to-access structures and processes. Their small-molecule dye is the first of its kind that can cross the blood-brain barrier, allowing researchers to differentiate between healthy brain tissue and a glioblastoma tumor in mice.
Rice University scientists get fungi to spill their secrets
As anyone who has ever attended a cocktail party can tell you, shedding inhibitions makes you more talkative and possibly more prone to divulging secrets. Fungi, it turns out, are no different from humans in this respect.

Lab lights way to simple chemical synthesis
Rice University scientists have developed a photochemical process to simplify the synthesis of drug and chemical precursors known as diamines.

More links aren’t necessarily better for hybrid nanomaterials
Chemists from Rice and the University of Texas have found more isn’t always better when it comes to packing charge acceptors atop nanocrystals.

Rice flashes new life into lithium-ion anodes
Rice chemists use flash Joule heating to recover graphite anodes from spent lithium-ion batteries.

US names two Rice students inaugural Quad Fellows
Two Rice graduate students are among the inaugural recipients of the Quad Fellowship.

Rice lab’s catalyst could be key for hydrogen economy
A light-activated catalyst efficiently converts ammonia into clean-burning hydrogen using only inexpensive raw materials.

Rice turns asphaltene into graphene for composites
The flash Joule heating process developed at Rice turns asphaltenes, a byproduct of crude oil production, into graphene for use in composite materials.

ACS taps Rice, Shell for Partners in Progress & Prosperity Award
Collaborators at Rice and Shell receive the American Chemical Society Southwest Regional Partners in Progress & Prosperity Award.