
Rice lab’s ‘drug factory’ implants cleared for human trials
Federal regulators have approved the first human clinical trial of cancer-killing “drug factory” implants created by Rice bioengineers.

Rice lab’s ‘drug factory’ implants cleared for human trials
Federal regulators have approved the first human clinical trial of cancer-killing “drug factory” implants created by Rice bioengineers.

Synthetic tools conduct messages from station to station in DNA
Bioengineers used deactivated Cas9 fusion proteins to synthetically control gene expression and reveal new details about natural processes in human cells.

Rice OEDK team creates new feeding device for Houston Zoo’s red river hogs
Just steps away from Rice University, you can meet Neptune, Luna, Vidalia, Artemis and Ophelia, the Houston Zoo’s resident red river hogs.

Rice bioengineers are shining light on bacterial stress
Rice bioengineers are ready to shine a lot of light on bacteria’s genetic response to stress.

CPRIT grants entice three cancer researchers to Rice
Rice University recruits three professors to bolster cancer research with grants from the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas.
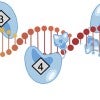
DAP array casts a wide net to fix mutations
Rice engineers introduce DAP, a streamlined CRISPR-based technology that can perform many genome edits at once to address polygenic diseases caused by more than one glitch.

Faculty recognized with award for superior teaching
Nine faculty received the 2022 George R. Brown Award for Superior Teaching, which honors top Rice instructors by votes from alumni who graduated within the past two, three and five years.

Faculty, staff, students honored for excellence in teaching, mentoring, service
Each year, Rice honors members of the university community who have served students through outstanding teaching, dedication and service.

NSF awards 38 Graduate Research Fellowships to Rice students
The National Science Foundation has awarded 38 Graduate Research Fellowships to Rice University students.

Rice trains postdocs for nano-cancer future
The National Institutes of Health extend a grant to help future medical professionals understand nanotechnology-enabled tools to treat cancer.
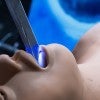
Inspired students make intubation more intuitive
Rice University engineering students develop a simplified, wireless video laryngoscope to help clinicians intubate patients before procedures or in an emergency.

Georgia Tech team wins Rice360 Design Competition
A Georgia Tech team won Rice360’s annual undergraduate design competition for global health technologies.

Blood vessels are guides for stimulating implants
A wireless neurostimulator a little bigger than a grain of rice can be put in place alongside blood vessels to treat neurological diseases and chronic pain.

US News grad school rankings give high marks to Rice programs
A total of 19 graduate programs at Rice University rank among the nation's top 25 in their categories in the latest edition of U.S. News and World Report’s “Best Graduate Schools.”

Bio-FlatScope dives deep for useful data
The lensless Bio-FlatScope is a small, inexpensive camera to monitor biological activity that can’t be captured by conventional instruments. The device could eventually be used to look for signs of cancer or sepsis or become a valuable endoscopy tool.