
Rice researchers helping to ready vote-by-mail system for November
Rice University researchers have won a federal grant to validate and improve VotingWorks' open-source vote-by-mail technology in time for November's election.
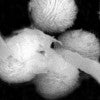
Better wastewater treatment? It’s a wrap
A shield of graphene helps particles destroy antibiotic-resistant bacteria and the free-floating genes in wastewater treatment plants.
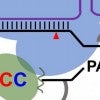
‘Bystander’ Cs meet their match in gene-editing technique
Biomolecular engineers at Rice have developed new tools to increase the accuracy of CRISPR single-base editing to treat genetic diseases.
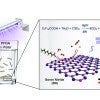
Boron nitride destroys PFAS 'forever' chemicals PFOA, GenX
Rice chemical engineers discovered a photocatalyst that can destroy 99% of the “forever” chemical PFOA

Future Texas hurricanes: Fast like Ike or slow like Harvey?
Climate change will make fast-moving storms more likely in late 21st-century Texas.

Laser-welded sugar: Sweet way to 3D-print blood vessels
Bioengineers keep cells alive in lab-grown tissues by creating networks of branching blood vessels from templates of 3D-printed sugar.
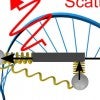
Cartwheeling light reveals new optical phenomenon
Researchers at Rice University have discovered details about a novel type of polarized light-matter interaction with light that literally turns end over end as it propagates from a source.

Purifying water with a partly coated gold nanoparticle
Rice's Naomi Halas has collaborated with Yale University engineers on the creation of a light-activated nanoparticle for clearing water of pollutants. The research is part of an effort by NEWT, the Rice-based Nanosystems Engineering Research Center for Nanotechnology-Enabled Water Treatment.
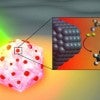
Fluorocarbon bonds are no match for light-powered nanocatalyst
Rice University engineers have created a light-powered catalyst that can break the strong chemical bonds in fluorocarbons, a group of synthetic materials that includes persistent environmental pollutants.
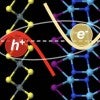
Excitons form superfluid in certain 2D combos
Mixing and matching computational models of 2D materials led scientists at Rice University to the realization that excitons can be manipulated in new and useful ways.
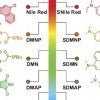
Rice lab turns fluorescent tags into cancer killers
Fluorophores with one oxygen atom replaced by a sulfur atom can be triggered with light to create reactive oxygen species within cancer cells, killing them.
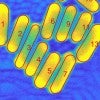
New tool helps nanorods stand out
Rice scientists introduce an open-source method to simplify nanoparticle analysis using scanning electron microscope images.

Rice team makes tiny, magnetically powered neural stimulator
Rice University neuroengineers have created a tiny surgical implant that can electrically stimulate the brain and nervous system without using a battery or wired power supply.

Rice scientist goes deep to improve environmental tracers
Rice Earth scientist Laurence Yeung earns a prestigious National Science Foundation CAREER Award to improve our understanding of the biosphere’s productivity.
