
Halas, Nordlander win prestigious Eni Energy Transition Award
Rice’s Naomi Halas and Peter Nordlander have won the prestigious 2022 Eni Energy Transition Award.

Halas, Nordlander win prestigious Eni Energy Transition Award
Rice’s Naomi Halas and Peter Nordlander have won the prestigious 2022 Eni Energy Transition Award.

Cherukuri named Rice University’s first vice president for innovation
Paul Cherukuri, the executive director of the Institute of Biosciences and Bioengineering, has been named Rice University’s first vice president for innovation.

Ramesh named Rice University’s vice president for research
Ramamoorthy Ramesh, a condensed matter physicist and materials scientist with more than 25 years in academia, industry, national labs and government service, has been named Rice University’s vice president for research.
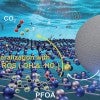
Rice improves catalyst that destroys ‘forever chemicals’ with sunlight
Rice chemical engineers have improved their light-powered catalyst for destroying forever chemical PFOA.
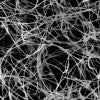
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real
Rice scientists create the first boron nitride nanotube fibers using the custom wet-spinning process they developed to make carbon nanotube fibers.
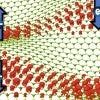
Bumps could smooth quantum investigations
Rice University materials theorists model a contoured surface overlaid with 2D materials and find it possible to control their electronic and magnetic properties. The discovery could simplify research into many-body effects, including quantum systems.
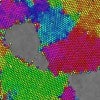
Grain boundaries go with the flow
Rice engineers mimic atom-scale grain boundaries with magnetic particles to see how shear stress influences their movement.

Cars could get a ‘flashy’ upgrade
Rice University chemists, working with the Ford Motor Company, processes waste plastic from end-of-life trucks into graphene for composite materials in new vehicles.

Rice ‘metalens’ could disrupt vacuum UV market
Rice photonics researchers have created a potentially disruptive technology for the ultraviolet optics market.

Rice scientists have developed an acid-based solvent that simplifies carbon nanotube processing.
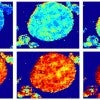
Lithium’s narrow paths limit batteries
Study suggests that lithium batteries would benefit from more porous electrodes with better-aligned particles that don’t limit lithium distribution.
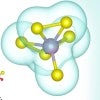
Rice lab improves recipe for valuable chemical
Rice University theorists show why salt gives a significant speed boost to valuable 2D molybdenum disulfide, an effect they say may work for other 2D materials as well.
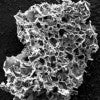
Treated plastic waste good at grabbing carbon dioxide
Rice University chemists treat waste plastic to absorb carbon dioxide from flue gas streams more efficiently than current processes.

Graphene gets enhanced by flashing
Rice University scientists who developed the flash Joule heating process to make graphene have found a way to produce doped graphene to customize it for applications.

Don’t underestimate undulating graphene
A theory by Rice University scientists suggests putting graphene on an undulating surface stresses it enough to create a minute electromagnetic field. The phenomenon could be useful for creating 2D electron optics or valleytronics devices.