
Rice scientist joins next Mars adventure
A Rice University geologist is one of 13 scientists recently selected to operate the Mars rover Perseverance and analyze samples for an eventual return to Earth.

Rice scientist joins next Mars adventure
A Rice University geologist is one of 13 scientists recently selected to operate the Mars rover Perseverance and analyze samples for an eventual return to Earth.
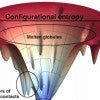
Understanding frustration could lead to better drugs
Atom-scale models of proteins that incorporate ligands, like drug molecules, show a strong correlation between minimally frustrated binding sites and drug specificity. Such models could lead to better-designed drugs with fewer side effects.

Rice Space Institute, Canada agree to collaborate
Rice Space Institute and the Consulate General of Canada in Dallas agree to collaborate on science and technology related to the space industry.

Voter research amid pandemic wins Rice students new national award
Undergrad team wowed judges by helping secure millions for polling place safety across Harris County.
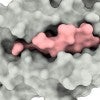
Once-discounted binding mechanism may be key to targeting viruses
Researchers detail subtle stabilizing effects in cells’ ability to recognize coronaviruses that compromise the immune system. The discovery could lead to new targets to prevent disease.
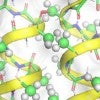
Folding proteins feel the heat, and cold
A new study shows proteins that presumably evolved to avoid water as they fold may actually behave in ways scientists did not anticipate.

Malaria test as simple as a bandage
HOUSTON – (Nov. 2, 2020) – Testing for malaria could become as simple as putting on a bandage.
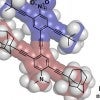
Rice rolls out next-gen nanocars
Rice researchers continue to advance the science of single-molecule machines with a new lineup of nanocars, in anticipation of the next international Nanocar Race in 2022.
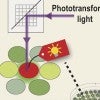
SPOTlight supercharges cell studies
Researchers develop a new method to isolate specific cells, and in the process find a more robust fluorescent protein.
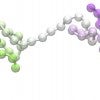
At our cores, we’re all strengthened by ‘dumbbells’
Scientists at Rice’s Center for Theoretical Biological Physics detail the structure of dumbbell-like sequences in DNA during interphase that suggest several unseen aspects of chromosome configuration and function.

Haotian Wang wins Packard Fellowship
Haotian Wang has been honored with a Packard Fellowship, one of 20 researchers in the nation to do so this year.

NSF renews Rice-based NEWT Center for water treatment
The National Science Foundation renews the Rice-based Nanotechnology Enabled Water Treatment Center for five years. The Engineering Research Center is dedicated to enabling access to clean water around the world.

Civil engineers Nagarajaiah, Erazo awarded Takuji Kobori Prize
Research on earthquake protection system earns prestigious award from the International Association for Structural Control and Monitoring.

Literal rise of the internet enables new climate science
Collaborative National Science Foundation grants will use data from internet balloons to study atmospheric gravity waves and their influence on the weather and climate.
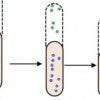
There’s a reason bacteria stay in shape
A primal mechanism in bacteria that keeps them in their personal Goldilocks zones -- that is, just right -- appears to depend on two random means of regulation, growth and division, that cancel each other out. The same mechanism may give researchers a new perspective on disease, including cancer.