
Tale of the tape: Sticky bits make better batteries
Rice University scientists use an industrial laser to turn adhesive tape into a component for safer, anode-free lithium metal batteries.

Tale of the tape: Sticky bits make better batteries
Rice University scientists use an industrial laser to turn adhesive tape into a component for safer, anode-free lithium metal batteries.
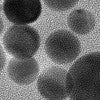
Charcoal a weapon to fight superoxide-induced disease, injury
Artificial enzymes made of treated charcoal could have the power to curtail damaging levels of superoxides that appear after an injury.
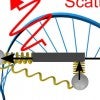
Cartwheeling light reveals new optical phenomenon
Researchers at Rice University have discovered details about a novel type of polarized light-matter interaction with light that literally turns end over end as it propagates from a source.

Tour scores prestigious Centenary Prize
Rice University chemist James Tour has been named a winner of this year’s Royal Society of Chemistry Centenary Prize.

Purifying water with a partly coated gold nanoparticle
Rice's Naomi Halas has collaborated with Yale University engineers on the creation of a light-activated nanoparticle for clearing water of pollutants. The research is part of an effort by NEWT, the Rice-based Nanosystems Engineering Research Center for Nanotechnology-Enabled Water Treatment.
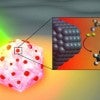
Fluorocarbon bonds are no match for light-powered nanocatalyst
Rice University engineers have created a light-powered catalyst that can break the strong chemical bonds in fluorocarbons, a group of synthetic materials that includes persistent environmental pollutants.
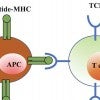
‘Relaxed’ T cells critical to immune response
Rice University researchers model the role of relaxation time as T cells bind to invaders or imposters, and how their ability to differentiate between the two triggers the body’s immune system.
Excitons form superfluid in certain 2D combos
Mixing and matching computational models of 2D materials led scientists at Rice University to the realization that excitons can be manipulated in new and useful ways.
Rice lab turns fluorescent tags into cancer killers
Fluorophores with one oxygen atom replaced by a sulfur atom can be triggered with light to create reactive oxygen species within cancer cells, killing them.
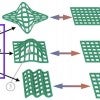
Lab makes 4D printing more practical
Soft robots and biomedical implants that reconfigure themselves upon demand are closer to reality with a method developed at Rice to print shapeshifting materials.
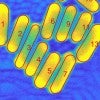
New tool helps nanorods stand out
Rice scientists introduce an open-source method to simplify nanoparticle analysis using scanning electron microscope images.

Egg-based coating preserves fresh produce
Eggs that would otherwise be wasted can be used as the base of an inexpensive coating to protect fruits and vegetables, according to Rice University researchers.

Exotic nanotubes move in less mysterious ways
Rice University researchers capture the first video of boron nitride nanotubes in motion to prove their potential for materials and medical applications.
2D sandwich sees molecules with clarity
A 2D platform of molybdenum, sulfur and selenium is adept at detecting biomolecules via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Its nonmetallic nature helps by curtailing background noise.

Rice faculty part of Baylor Superfund program
A $10 million federal grant establishes a center to study how toxic chemicals from Superfund sites impact preterm births.