Heart nanofiber project makes STAT Madness round 3
A Texas Heart Institute/Rice project to use nanotube fibers to repair damaged hearts advances to round 3 of STAT Madness.

Heart nanofiber project makes STAT Madness round 3
A Texas Heart Institute/Rice project to use nanotube fibers to repair damaged hearts advances to round 3 of STAT Madness.
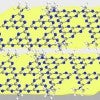
New nano strategy fights superbugs
Rice researchers imprint carbon nitride nanosheets to catch and kill free-floating antibiotic resistant genes found in secondary effluent produced by wastewater treatment plants. The strategy would prevent the DNA molecules from making downstream bacteria more resistant to drugs.

Natural bayou better when floods threaten Houston
A comparison of flood plains around Houston’s two major bayous shows the natural Buffalo Bayou is far better at managing floodwaters than the channelized Brays Bayou.
Strong signals show how proteins come and go
Rice University bioscientists develop a versatile gene signal amplifier that can not only do a better job of detecting the expression of chromosomal genes than current methods but can potentially be used to detect any cellular gene.

Heart nanofibers make STAT Madness Round 2
The Rice/Texas Heart Institute project to use nanotube fibers to repair damaged hearts makes Round 2 of STAT Madness.

Robert Ladd elected Rice Board of Trustees chair
Rice University alumnus Robert T. Ladd ’78 has been elected chair of the Rice Board of Trustees, effective July 1.
Tissue-digging nanodrills do just enough damage
Scientists at Rice and their collaborators show light-activated molecular drills effectively kill cells in whole eukaryotic organisms.
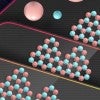
A small step for atoms, a giant leap for microelectronics
Rice materials scientist Boris Yakobson and colleagues in Taiwan and China report in Nature on making large single-crystal sheets of hexagonal boron nitride, touted as a key insulator in future two-dimensional electronics.
‘Smart water’ may aid oil recovery
Rice University engineers study the mechanism that would allow “smart water" to aid oil recovery from reservoirs.
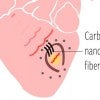
Heart nanofiber breakthrough awaits your STAT Madness vote
Joint Texas Heart Institute/Rice University research into using carbon nanotube fibers to bridge damaged areas of hearts is part of this year's STAT Madness, a competition to choose the year's best university-based bioscience project.
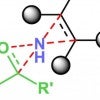
Rice scientists simplify access to drug building block
Rice University chemists further simplify their process to make essential precursor molecules for drug discovery and manufacture. The method to modify unactivated olefins for use as building blocks could save the pharmaceutical industry millions.

Rice hosts middle schoolers for Engineers Week
Houston middle-school students visit Rice to take part in Engineers Week.

CPRIT grant draws cell imaging specialist to Rice
The Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas awards a $2 million grant to Rice to recruit physical chemist Anna-Karin Gustavsson, who will study the dynamics and distributions of single molecules in living cells through her development of sophisticated imaging systems.

Magnet-controlled bioelectronic implant could relieve pain
A Rice electrical and computer engineer has introduced the first neural implant that can be programmed and charged remotely with a magnetic field.

Rice kinesiologists found specific health deficits in home-schooled adolescents compared to their peers in public schools.