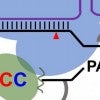
‘Bystander’ Cs meet their match in gene-editing technique
Biomolecular engineers at Rice have developed new tools to increase the accuracy of CRISPR single-base editing to treat genetic diseases.

‘Bystander’ Cs meet their match in gene-editing technique
Biomolecular engineers at Rice have developed new tools to increase the accuracy of CRISPR single-base editing to treat genetic diseases.

Bird droppings carry risk of antibiotic resistance
Rice University engineers analyze the droppings of urban birds and show persistent levels of antibiotic-resistant genes and bacteria that may be transferred to humans through the environment.
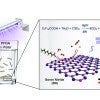
Boron nitride destroys PFAS 'forever' chemicals PFOA, GenX
Rice chemical engineers discovered a photocatalyst that can destroy 99% of the “forever” chemical PFOA

Future Texas hurricanes: Fast like Ike or slow like Harvey?
Climate change will make fast-moving storms more likely in late 21st-century Texas.

Laser-welded sugar: Sweet way to 3D-print blood vessels
Bioengineers keep cells alive in lab-grown tissues by creating networks of branching blood vessels from templates of 3D-printed sugar.
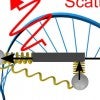
Cartwheeling light reveals new optical phenomenon
Researchers at Rice University have discovered details about a novel type of polarized light-matter interaction with light that literally turns end over end as it propagates from a source.

Study finds new link between Alzheimer’s suspects
Researchers have described for the first time specific genes and pathways in the brain associated with Alzheimer’s disease.

Rice lab’s bright idea is pure gold
Physicists discover plasmonic metals can produce “hot carriers” that emit unexpectedly bright light in nanoscale gaps between electrodes.

Rice shares grant for AI-driven COVID-19 research
Todd Treangen received a C3.ai Digital Transformation Institute Award for computational biology research to apply AI models to COVID-19 mitigation.

Purifying water with a partly coated gold nanoparticle
Rice's Naomi Halas has collaborated with Yale University engineers on the creation of a light-activated nanoparticle for clearing water of pollutants. The research is part of an effort by NEWT, the Rice-based Nanosystems Engineering Research Center for Nanotechnology-Enabled Water Treatment.
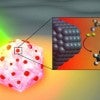
Fluorocarbon bonds are no match for light-powered nanocatalyst
Rice University engineers have created a light-powered catalyst that can break the strong chemical bonds in fluorocarbons, a group of synthetic materials that includes persistent environmental pollutants.

NSF RAPID grant supports COVID-19 'computational pipeline'
Lydia Kavraki wins a NSF Rapid Response Research grant to help identify SARS-CoV-2 viral proteins for vaccine development.
Excitons form superfluid in certain 2D combos
Mixing and matching computational models of 2D materials led scientists at Rice University to the realization that excitons can be manipulated in new and useful ways.

Higgs addresses RCEL students; Engineering shares anti-racism resources
Find reading lists and toolkits for allies, information on self-care and ways to get involved in social justice initiatives.

Rice engineers offer smart, timely ideas for AI bottlenecks
Rice researchers demonstrate methods to design data-centric hardware and co-designing hardware with machine-learning algorithms that can improve energy efficiency in artificial intelligence hardware.