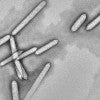
Rice bioengineers developed a new genetic regulatory system that makes the production of gas vesicles more sustainable for nonnative host cells.

Rice bioengineers developed a new genetic regulatory system that makes the production of gas vesicles more sustainable for nonnative host cells.

Materials that match the brain: Rice engineer earns Sontag Foundation distinction
Rice materials scientist and neuroengineer Christina Tringides has been named a Distinguished Scientist by the Sontag Foundation, a national recognition for early career researchers advancing transformative projects in brain cancer research.
Rice establishes Amyloid Research Center to tackle neurodegenerative diseases
Rice has launched the Amyloid Mechanism and Disease Center, a new campus hub dedicated to uncovering the molecular origins of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and other amyloid-related diseases.

Rice study reveals Parkinson’s protein clumps rob brain cells of vital energy
A new study has revealed that protein clumps associated with Parkinson’s can actively drain energy from brain cells.

Brain inflammation treatment could be ally in fight against dementia
Scientists from Rice and Houston Methodist have developed a new way to reduce inflammation in the brain, a discovery that could help fight diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.

Rice scientists develop hydrogel platform for long-lasting, precision drug delivery
Rice scientists have developed a new drug delivery platform that could make it easier for patients to take their medications and may even boost drug efficacy.

Rice research team on quest to engineer computing systems from living cells
A Rice research team is on quest to engineer computing systems from living cells.

Common food bacteria could help make vitamins cheaper, greener
A new study reveals how L. lactis regulates the production of a key precursor in vitamin K₂ biosynthesis.

‘Major leap in bioelectronic sensing’: Rice researchers turn bacteria into tiny pollution detectors
A study led by Xu Zhang, Marimikel Charrier and Caroline Ajo-Franklin demonstrates an innovative method for the real-time, on-site detection of arsenite and cadmium.

Computational biochemist joins Rice with CPRIT recruitment award
Computational biochemist Linna An will join Rice’s Department of Biosciences with support from a $2 million award from the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas.

Rice bioengineer looks to mitochondria as key to heart failure recovery
Rice bioengineer Mario Escobar has won a Transformational Project Award from the American Heart Association to develop a new therapy for heart failure.

Cancer Bioengineering Collaborative kicks off seminar series with Nobel laureate James Allison
The Cancer Bioengineering Collaborative launched its inaugural seminar June 3 with an invited talk from Nobel laureate James P. Allison.

Targeting mitochondria to fight leukemia: Rice-led research team pursues new treatment strategies
Acute myeloid leukemia remains one of the most aggressive and deadly forms of blood cancer, even as treatments have advanced in recent years.

Rice researchers engineer personalized treatments for movement impairments
Impaired neuromusculoskeletal function due to conditions such as stroke, osteoarthritis, cerebral palsy, Parkinson’s disease, limb amputation, spinal cord injury, traumatic brain injury and cancer is a leading cause of disability.

Rice statistician earns CPRIT award to advance AI-powered precision medicine for prostate cancer
Rice statistician Erzsébet Merényi is part of a team of researchers awarded $1 million by the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas to develop AI tools that can identify lethal forms of prostate cancer earlier and improve treatment selection.