Rice University on winter break Dec. 23-Jan. 4
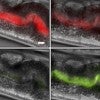
Light flips genetic switch in bacteria inside transparent worms
Researchers from Rice University and Baylor College of Medicine have shown that colored light can both activate and deactivate genes of gut bacteria in the intestines of worms. The research shows how optogenetic technology can be used to investigate the health impacts of gut bacteria.
Rice offers visiting students online summer classes for credit

AI-powered microscope could check cancer margins in minutes
Researchers from Rice University and MD Anderson Cancer Center have created a microscope that uses artificial intelligence to quickly and inexpensively image large tissue sections at high resolution with minimal preparation. If clinically validated, the DeepDOF microscope could allow surgeons to inspect tumor margins within minutes.
Weak force has strong impact on nanosheets
Dogtrot dwelling divides to conquer energy bills
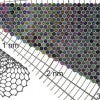
Sheets of carbon nanotubes come in a rainbow of colors
Nanomaterials researchers in Finland, the United States and China have created a color atlas for 466 unique varieties of single-walled carbon nanotubes.

Drop in activity along border could cost Texas billions, says Baker Institute expert
The reduction in mobility along the Texas-Mexico border caused by COVID-19 will hurt the state's economy as a whole, according to new research from Rice University’s Baker Institute for Public Policy.
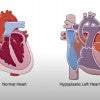
Top Rice data science team shows heart in plan to save babies
Winning Data to Knowledge Lab project uses data science techniques to help save babies with congenital heart defects.

Bad news for fake news: Rice research helps combat social media misinformation
Improved use of machine learning can double throughput of real-time information filters, Rice researchers find.

Rice's Pumani hailed for reaching 1 million babies
Rice global health institute's low-cost, neonatal CPAP joins Global Innovation Exchange's Million Lives Club.

Religious discrimination particularly high for Jews and Muslims, study shows
HOUSTON – (Dec. 9, 2020) – Although people of all faiths report growing religious discrimination during the past few years, the phenomenon is most common among Jews and Muslims, according to a new study from researchers at Rice University and West Virginia University (WVU). In addition, Jews and Muslims are much more likely to become victims of violence because of their religious beliefs.

Texas lawmakers see vaccine legislation as nonpartisan
Vaccine-related legislation should be promoted as nonpartisan, new research suggests, and most Texas lawmakers agree despite a vocal anti-vaccine movement.
