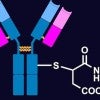
Targeted tumors attack not-innocent bystanders
Antibody-drug conjugates developed are found to attack not only targeted tumor cells but also nontargeted “bystanders.”

Targeted tumors attack not-innocent bystanders
Antibody-drug conjugates developed are found to attack not only targeted tumor cells but also nontargeted “bystanders.”
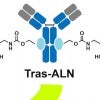
Drug doubles down on bone cancer, metastasis
Researchers at Rice University and Baylor College of Medicine develop an antibody conjugate called BonTarg that delivers drugs to bone tumors and inhibits metastasis.

Scientists seek details of cancer’s evolutionary tree
Rice University computer scientists will take full advantage of new technology to sequence the genome of a single cell to decode mysteries contained in tumors.
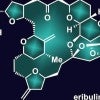
Reversal speeds creation of important molecule
A Rice lab’s reverse approach to making halichondrin B is the shortest route to a “rather complex and important molecule."

Study examines how breast implant surfaces affect immune response
Rice University bioengineers collaborated on a six-year study that systematically analyzed how the surface architecture of silicone breast implants influences adverse side effects.

NIH grant boosts computational search for cancer drugs
Computer scientist Lydia Kavraki of Rice University’s Brown School of Engineering has won a prestigious National Institutes of Health U01 grant to develop a new approach to model and analyze protein-ligand interactions in cancer research.

NIH supports mathematical optimization of tumor treatment
A new strategy to reduce the side effects suffered by patients undergoing treatment for head and neck cancers now has the support of the National Institutes of Health.

Biologists construct a ‘periodic table’ for cell nuclei
A team of biologists studying the tree of life has unveiled a new classification system for cell nuclei, and discovered a method for transmuting one type of cell nucleus into another.

Feds back probe of understudied gut nervous system
Rice University neurobiologist Rosa Uribe has won a five-year, $2 million R01 grant from the National Institutes of Health to study how the enteric nervous system develops.
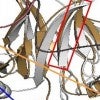
Cancer ‘guardian’ breaks bad with one switch
A mutation that replaces a single amino acid in a potent tumor-suppressing protein makes it prone to nucleating amyloid fibrils implicated in many cancers as well as neurological diseases.

Cerium sidelines silver to make drug precursor
Rice scientists have developed a simplified method to make fluoroketones, a drug precursor that typically requires an expensive silver catalyst.
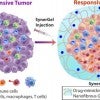
UTHealth, Rice advance oral cancer immunotherapy
Researchers at Rice and the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston develop a hydrogel that could destroy oral cancer tumors.

AI-powered microscope could check cancer margins in minutes
Researchers from Rice University and MD Anderson Cancer Center have created a microscope that uses artificial intelligence to quickly and inexpensively image large tissue sections at high resolution with minimal preparation. If clinically validated, the DeepDOF microscope could allow surgeons to inspect tumor margins within minutes.
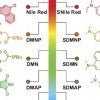
Rice lab turns fluorescent tags into cancer killers
Fluorophores with one oxygen atom replaced by a sulfur atom can be triggered with light to create reactive oxygen species within cancer cells, killing them.
Machine learning can help increase liver cancer screening rates, says Rice expert
Targeting patients with machine learning can increase the number of people getting liver cancer screenings, according to a National Institutes of Health-sponsored study by a research team from Rice, Texas A&M University, Iowa State University and the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center.