
Woven nanotube fibers turn heat into power
Carbon nanotubes woven into thread-like fibers and sewn into fabrics become a thermoelectric generator that can turn heat from the sun or other sources into energy.

Woven nanotube fibers turn heat into power
Carbon nanotubes woven into thread-like fibers and sewn into fabrics become a thermoelectric generator that can turn heat from the sun or other sources into energy.

NSF grant kicks off Center for Adapting Flaws into Features
Rice University has won a Phase I National Science Foundation grant to establish the NSF Center for Adapting Flaws into Features to investigate nanoscale chemical phenomena and optimize the structures and electronic properties of materials.
Programmed bacteria have something extra
Rice chemists expand genetic code of E. coli to produce 21st amino acid, giving it new abilities.
Targeted tumors attack not-innocent bystanders
Antibody-drug conjugates developed are found to attack not only targeted tumor cells but also nontargeted “bystanders.”
Drug doubles down on bone cancer, metastasis
Researchers at Rice University and Baylor College of Medicine develop an antibody conjugate called BonTarg that delivers drugs to bone tumors and inhibits metastasis.

NIH grant will help streamline chemical synthesis
Rice University chemist Julian West has won a five-year, $1.8 million National Institutes of Health grant to advance his lab’s efforts to simplify the synthesis of organic chemicals.
Reversal speeds creation of important molecule
A Rice lab’s reverse approach to making halichondrin B is the shortest route to a “rather complex and important molecule."
‘Flashed’ nanodiamonds are just a phase
The “flash” process developed at Rice University can turn carbon black into functionalized nanodiamond and other materials. The carbon atoms evolved through several phases depending on the length of the flash.

Sickle cell advance incorporates Rice lab's tech
Rice University bioengineer Gang Bao, a pioneer in the search for a way to treat and perhaps cure sickle cell disease, is co-author of a significant step forward revealed in Science Translational Medicine and led by his colleagues at Stanford University.
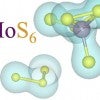
Rice lab peers inside 2D crystal synthesis
Scientific studies describing the most basic processes often have the greatest impact in the long run. A new work by Rice University engineers could be one such, and it’s a gas, gas, gas for nanomaterials.

People, papers and presentations - May 28, 2021
People, papers and presentations - May 28, 2021

Biologists construct a ‘periodic table’ for cell nuclei
A team of biologists studying the tree of life has unveiled a new classification system for cell nuclei, and discovered a method for transmuting one type of cell nucleus into another.

In graphene process, resistance is useful
Lab uses laser-induced graphene process to create micron-scale patterns in photoresist for consumer electronics and more.

Rice names architect for new engineering and science building
With the imminent demolition of Rice University’s Abercrombie Engineering Laboratory, the space will soon be cleared for a new engineering and science building, according to Rice administrators. International architecture firm Skidmore, Owings & Merrill (SOM) has been selected as lead architect for the new building. Houston’s Scientia Architects will consult on laboratory design.
Silver ions hurry up, then wait as they disperse
There’s gold in them thar nanoparticles, and there used to be a lot of silver, too. But much of the silver has leached away, and researchers want to know how.