A team of chemists and bioengineers at Rice University and the University of Houston have achieved a significant milestone in their work to create a biomaterial that can be used to grow biological tissues outside the human body. The development of a novel fabrication process to create aligned nanofiber hydrogels could offer new possibilities for tissue regeneration after injury and provide a way to test therapeutic drug candidates without the use of animals.
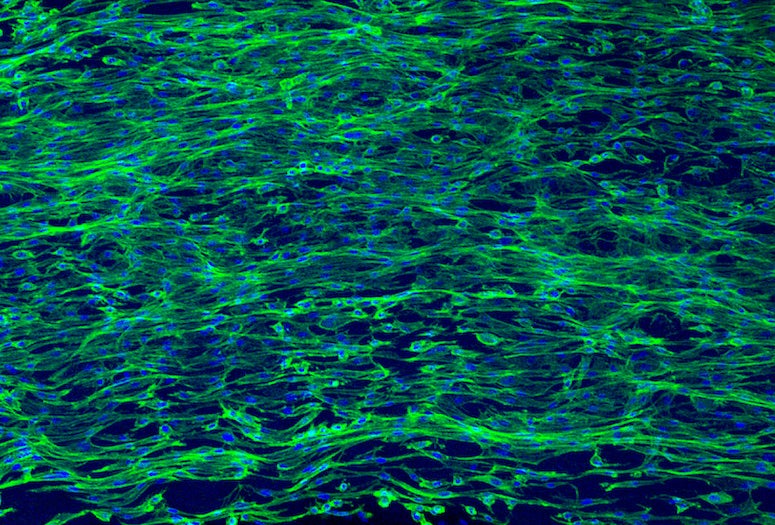
The research team, led by Jeffrey Hartgerink, professor of chemistry and bioengineering, has developed peptide-based hydrogels that mimic the aligned structure of muscle and nerve tissues. Alignment is critical for the tissues’ functionality, but it is a challenging feature to reproduce in the lab, as it entails lining up individual cells.
For over ten years, the team has been designing multidomain peptides (MDPs) that self-assemble into nanofibers. These resemble the fibrous proteins found naturally in the body, much like a spiderweb at nanoscale.
In their latest study, published online and featured on the cover of the journal ACS Nano, the researchers discovered a new method to create aligned MDP nanofiber “noodles.” By first dissolving the peptides in water and then extruding them into a salty solution, they were able to create aligned peptide nanofibers – like twisted strands of rope smaller than a cell. By increasing the concentration of ions, or salt, in the solution and repeating the process, they achieved even greater alignment of the nanofibers.
“Our findings demonstrate that our method can produce aligned peptide nanofibers that effectively guide cell growth in a desired direction,” explained lead author Adam Farsheed, who recently received his Ph.D. in bioengineering from Rice. “This is a crucial step toward creating functional biological tissues for regenerative medicine applications.”
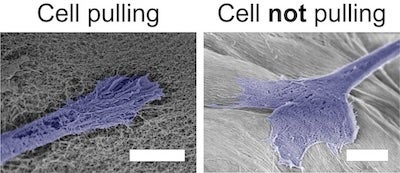
One of the key findings of the study was an unexpected discovery: When the alignment of the peptide nanofibers was too strong, the cells no longer aligned. Further investigation revealed that the cells needed to be able to “pull” on the peptide nanofibers to recognize the alignment. When the nanofibers were too rigid, the cells were unable to exert this force and failed to arrange themselves in the desired configuration.
“This insight into cell behavior could have broader implications for tissue engineering and biomaterial design,” said Hartgerink. “Understanding how cells interact with these materials at the nanoscale could lead to more effective strategies for building tissues.”
Additional study co-authors from Rice include chemistry department Ph.D. graduates Tracy Yu and Carson Cole, graduate student Joseph Swain, and undergraduate researcher Adam Thomas. Bioengineering undergraduate researcher Jonathan Makhoul, graduate student Eric Garcia Huitron, and Professor K. Jane Grande-Allen were also co-authors on the study. The team of researchers from the University of Houston includes Ph.D. student Christian Zevallos-Delgado, research assistant Sajede Saeidifard, research assistant professor Manmohan Singh and engineering professor Kirill Larin.
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01DE021798, R01EY022362, R01HD095520, R01EY030063), the National Science Foundation (2129122), the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program, and the Welch Foundation (C-2141). The content in this news release is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the funding organizations.
- Peer-reviewed paper:
-
Tunable macroscopic alignment of self-assembling peptide nanofibers | ACS Nano | DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.4c02030
Authors: Adam Farsheed, Christian Zevallos-Delgado, Tracy Yu, Sajede Saeidifard, Joseph Swain, Jonathan Makhoul, Adam Thomas, Carson Cole, Eric Garcia Huitron, Kathryn Jane Grande-Allen, Manmohan Singh, Kirill Larin and Jeffrey Hartgerink
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.4c02030 - Video is available at:
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M4KNgNZi-YI
Description: Aligned peptide “noodle” fabrication process.
- Image downloads:
-
https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2024/05/Fig1-0a8c0263b96fee0b.jpg
CAPTION: Scanning electron micrographs of MDP nanofibers of increasing alignments (scale bars = 500 nanometers). (Image courtesy of Adam Farsheed/Rice University)
https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2024/05/Fig2-74d0049e3af4946e.jpg
CAPTION: Confocal micrographs of cells spreading on aligned MDP “noodles.” Cell nuclei are stained blue and actin is stained green (scale bar = 500 micrometers). (Image courtesy of Adam Farsheed/Rice University)
https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2024/05/Fig3-76ea1c8e19a585f8.jpg
CAPTION: Scanning electron micrographs of cells pulling on nanofibers with lower alignments, but not pulling on nanofibers with higher alignments. Cells are falsely colored blue (scale bars = 5 micrometers). (Image courtesy of Adam Farsheed/Rice University)
https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2024/05/Hartgerink_Farsheed-4e1d94d16605710b.jpg
CAPTION: Jeffrey Hartgerink (left) is a professor of chemistry and bioengineering and associate chair for undergraduate studies. Adam Farsheed is a bioengineering doctoral alum and the lead author on the study. (Photo by Gustavo Raskosky/Rice University)