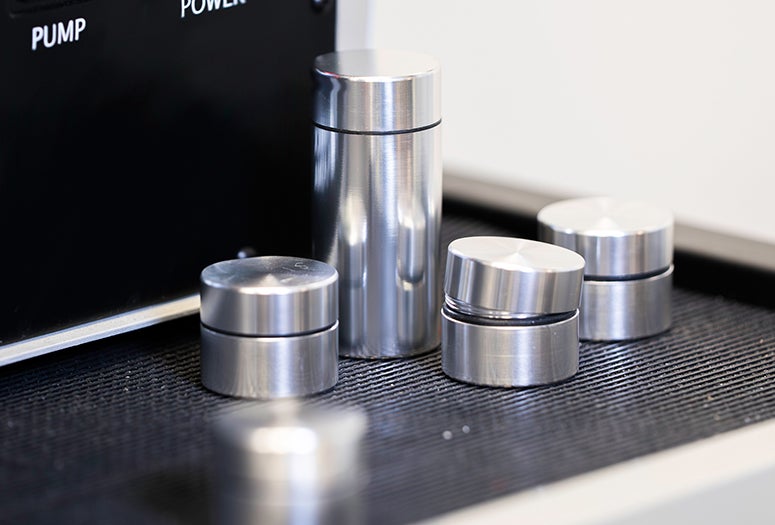
Rice University engineers have created containers that can keep volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from accumulating on the surfaces of stored nanomaterials.
The portable and inexpensive storage technology addresses a ubiquitous problem in nanomanufacturing and materials science laboratories and is described in a paper published this week in the American Chemical Society journal Nano Letters.
“VOCs are in the air that surrounds us every day,” said study corresponding author Daniel Preston, an assistant professor in Rice’s Department of Mechanical Engineering. “They cling to surfaces and form a coating, primarily of carbon. You can’t see these layers with the naked eye, but they form, often within minutes, on virtually any surface exposed to air.”

VOCs are carbon-based molecules that are emitted from many common products, including cleaning fluids, paints, and office and crafting supplies. They accumulate indoors in particularly high concentrations, and the thin layers of carbon gunk they deposit on surfaces can hinder industrial nanofabrication processes, limit the accuracy of microfluidic testing kits and produce confusion for scientists who conduct fundamental research on surfaces.
To address the problem, Ph.D. student and study lead author Zhen Liu, together with Preston and others from his lab, developed a new type of storage container that keeps objects clean. Experiments showed that her approach effectively prevented surface contamination for at least six weeks and could even clean VOC-deposited layers from previously contaminated surfaces.
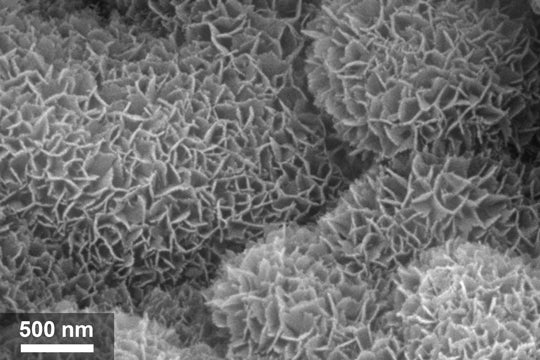
The technology relies on an ultraclean wall inside the container. The surface of the interior wall is enhanced with tiny bumps and divots ranging in size from a few millionths to a few billionths of a meter. The microscopic and nanoscopic imperfections increase the wall’s surface area, making more of its metal atoms available to VOCs in air that’s inside the containers when they are sealed.
“The texturing allows the internal container wall to act as a ‘sacrificial’ material,” Liu said. “VOCs are pulled onto the surface of the container wall, which allows other objects stored inside to remain clean.”
She said the idea of using a large precleaned surface to accumulate pollutants was proposed 50 years ago but went largely unnoticed. She and her colleagues improved on the idea with modern methods of cleaning and nanotexturing surfaces. They showed, through a series of experiments, that their approach did a better job of preventing VOCs from coating the surfaces of stored materials than other approaches, including sealed petri dishes and state-of-the-art vacuum desiccators.
Preston’s group built on its experiments, developing a theoretical model that accurately characterized what was happening inside the containers. Preston said the model will allow them to refine their designs and optimize system performance in the future.
The research was supported by Rice’s Shared Equipment Authority, the Rice University Academy of Fellows, the United States Coast Guard Advanced Education Program and an Innovation in Buildings fellowship from the Department of Energy (DE-SC0014664).
- Peer-reviewed paper
-
“Mitigating Contamination with Nanostructure-Enabled Ultraclean Storage” | Nano Letters | DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c00626
Authors: Zhen Liu, Te Faye Yap, Anoop Rajappan, Rachel A. Shveda, Rawand M. Rasheed and Daniel J. Preston
- Image downloads
-
https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2023/07/0717_CLEAN_GR03xc-lg.jpg
CAPTION: Mechanical engineers in Rice University’s Preston Innovation Laboratory have created containers that can keep volatile organic compounds from accumulating on the surfaces of stored nanomaterials. (Photo by Gustavo Raskosky/Rice University)https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2023/07/0717_CLEAN_GR09-ZL-lg.jpg
CAPTION: Rice University Ph.D. student Zhen Liu and colleagues in the Department of Mechanical Engineering’s Preston Innovation Laboratory developed container technology that can prevent volatile organic compounds from coating the surface of stored objects for at least six weeks. (Photo by Gustavo Raskosky/Rice University)https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2023/07/0717_CLEAN-sem3x2-lg.jpg
CAPTION: A scanning electron microscope image (scale bar is 500 billionths of a meter in length) reveals myriad imperfections like those that Rice University engineers created on the interior walls of materials storage containers. The imperfections keep the surfaces of stored materials clean by attracting volatile organic compounds from air that gets sealed inside the containers. (Image courtesy of Preston Innovation Laboratory/Rice University)https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2023/07/0717_CLEAN_GR12-zldp-lg.jpg
CAPTION: Zhen Liu (left), a Ph.D. student in mechanical engineering at Rice University, and Daniel Preston, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering at Rice, teamed with others from Preston’s laboratory to create storage technology that can keep volatile organic compounds from accumulating on stored surfaces. (Photo by Gustavo Raskosky/Rice University) - Related stories
-
Fluidic circuits add analog options for controlling soft robots – Sept. 28, 2022
https://news.rice.edu/news/2022/fluidic-circuits-add-analog-options-controlling-soft-robotsWearables take ‘logical’ step toward onboard control – Aug. 30, 2022
https://news.rice.edu/news/2022/wearables-take-logical-step-toward-onboard-controlPowering an ‘arm’ with air could be mighty handy – Aug. 25, 2022
https://news.rice.edu/news/2022/powering-arm-air-could-be-mighty-handyRice engineers get a grip with ‘necrobotic’ spiders – July 25, 2022
https://news.rice.edu/news/2022/rice-engineers-get-grip-necrobotic-spidersDaniel Preston wins NSF CAREER Award – May 6, 2022
https://news.rice.edu/news/2022/daniel-preston-wins-nsf-career-award - Links
-
Preston Innovation Laboratory: https://pi.rice.edu
Department of Mechanical Engineering: https://mech.rice.edu
George R. Brown School of Engineering: https://engineering.rice.edu
- About Rice
-
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 4,240 undergraduates and 3,972 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 4 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.

