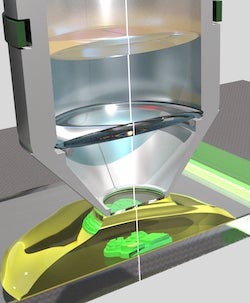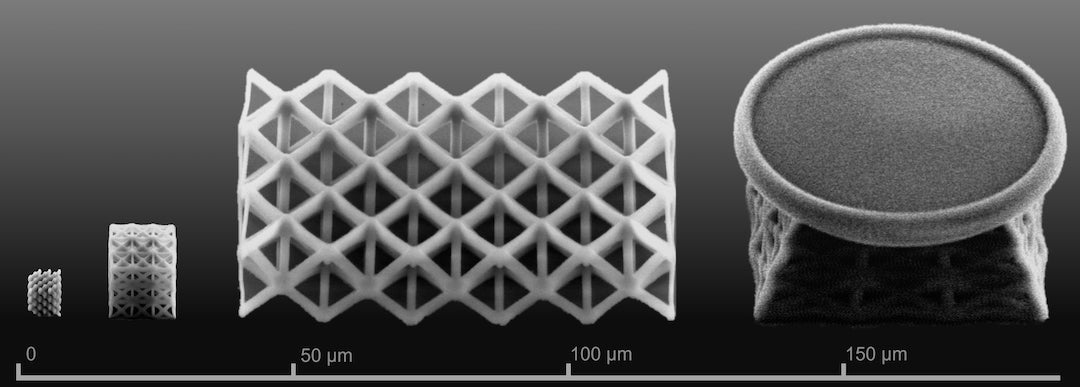
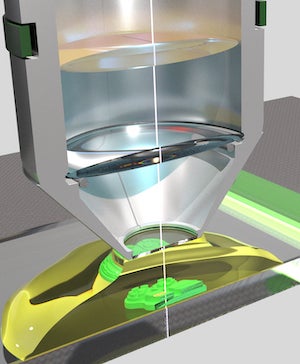
Weaving intricate, microscopic patterns of crystal or glass is now possible thanks to engineers at Rice University.
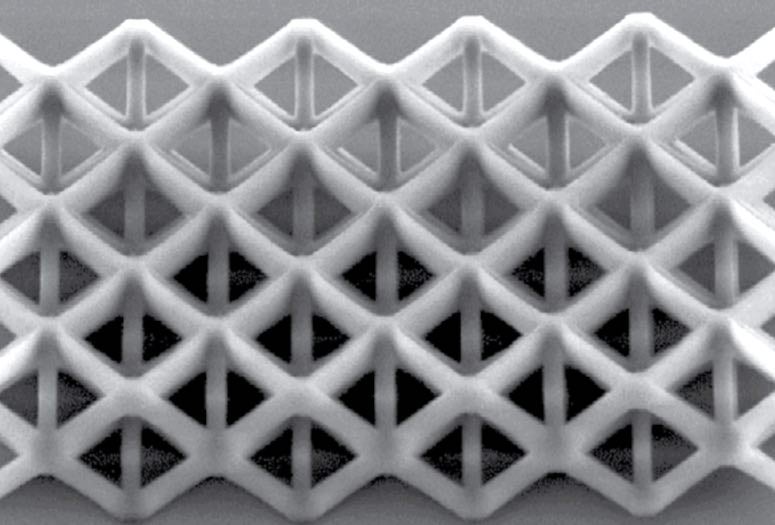
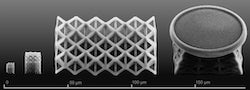
Rice materials scientists are creating nanostructures of silica with a sophisticated 3D printer, demonstrating a method to make micro-scale electronic, mechanical and photonic devices from the bottom up. The products can be doped and their crystal structures tuned for various applications.
The study led by Jun Lou, a professor of materials science and nanoengineering at the George R. Brown School of Engineering, appears in Nature Materials.
The electronics industry is built upon silicon, the basic semiconducting substrate for microprocessors for decades. The Rice study addresses the limitations of top-down manufacturing by turning the process on its head.
“It’s very tough to make complicated, three-dimensional geometries with traditional photolithography techniques,” Lou said. “It’s also not very ‘green’ because it requires a lot of chemicals and a lot of steps. And even with all that effort, some structures are impossible to make with those methods.
“In principle, we can print arbitrary 3D shapes, which could be very interesting for making exotic photonic devices,” he said. “That’s what we’re trying to demonstrate.”
The lab uses a two-photon polymerization process to print structures with lines only several hundred nanometers wide, smaller than the wavelength of light. Lasers “write” the lines by prompting the ink to absorb two photons, initiating free-radical polymerization of the material.
“Normal polymerization involves polymer monomers and photoinitiators, molecules that absorb light and generate free radicals,” said Rice graduate student and co-lead author Boyu Zhang of the process that commonly uses ultraviolet light in 3D printing and to cure coatings and in dental applications.
“In our process, the photoinitiators absorb two photons at the same time, which requires a lot of energy,” he said. “Only a very small peak of this energy causes polymerization, and that in only a very tiny space. That’s why this process allows us to go beyond the diffraction limit of light.”

The printing process required the Rice lab to develop a unique ink. Zhang and co-lead author Xiewen Wen, a Rice alumnus, created resins containing nanospheres of silicon dioxide doped with polyethylene glycol to make them soluble.
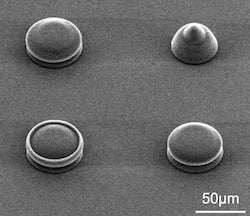
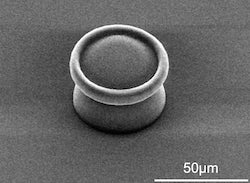
After printing, the structure is solidified through high-temperature sintering, which eliminates all the polymer from the product, leaving amorphous glass or polycrystalline cristobalite. “When heated, the material goes through phases from glass to crystal, and the higher the temperature, the more ordered the crystals become,” Lou said.
The lab also demonstrated doping the material with various rare earth salts to make the products photoluminescent, an important property for optical applications. The lab’s next goal is to refine the process to achieve sub-10 nanometer resolution.
Co-authors of the paper are Rice assistant research professor Hua Guo, research scientists Guanhui Gao and Xiang Zhang, alumnus Yushun Zhao and graduate students Qiyi Fang and Christine Nguyen; Rice alumnus Fan Ye of Tsinghua University, Beijing; University of Houston alumnus Shuai Yue, now a postdoctoral researcher at the Chinese Academy of Sciences; and Jiming Bao, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at the University of Houston.
Co-principal investigators are Rice alumnus Weipeng Wang, now a professor at Tsinghua University, China; and Rice’s Jacob Robinson, an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering and of bioengineering, and Pulickel Ajayan, chair of the Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering, the Benjamin M. and Mary Greenwood Anderson Professor in Engineering and a professor of chemistry.
The Welch Foundation (C-1716, E-1728) supported the research.